
views
Thyroid dysfunction is one of the most common hormonal conditions that affect women of reproductive age most frequently. Various studies have shown that there is a link between thyroid dysfunction and reproductive potential in both males and females.
Hypothyroidism is associated with irregular menstrual cycles, subfertility (difficulty conceiving), miscarriage, pregnancy complications, and an increased risk for structural and functional disabilities in the unborn child.
Planning to have children and becoming pregnant also means getting familiar with your own body and health, this results in uncovering and learning about various bodily functions and the kind of bearing they can have on your or your partner’s fertility health. The thyroid is among these bodily functions and at times its correlation with fertility health is downplayed, which should not be acceptable.
It is a frequent issue and often an unidentified contributing factor in cases of unexplained infertility.
One of the most frequent hormonal conditions affecting women of reproductive age is caused by a thyroid disorder, Dr Rubina Pandit Fertility Consultant, Nova IVF Fertility, Basaveshwaranagar, Bangalore, and Dr Anitha B.R, Senior Consultant Obstetrician, Gynecologist & Fertility specialist, Scientific Director, IVF, Motherhood Hospitals, Whitefield, Bangalore classify thyroid conditions that impair fertility
- Hypothyroidism is a disorder caused by decreased thyroid hormone production where patients can present with various symptoms like lethargy, hot or cold intolerance, weight gain, etc.
- Hyperthyroidism: Also known as an overactive thyroid, hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, which speeds up the body’s metabolism and causes a number of symptoms such as weight loss, and irregular or rapid heartbeat.
- Autoimmune thyroid disease (with normal thyroid function): Proper evaluation by a reproductive endocrinologist is always advised before starting any medications.
Thyroid disorders refer to a group of disorders that cause dysregulated functions of the thyroid gland resulting in overproduction (Hyperthyroidism) or underproduction (Hypothyroidism) of thyroid hormones (Tri iodothyronine T3 and thyroxine T4)
Hypo or Hyperthyroidism can each negatively impact fertility by both the ability to get pregnant and carry a foetus to term. Both conditions cause Irregular menses, making it harder to predict ovulation, interference with the release of an egg from the ovary (Ovulation), increased risk of miscarriages due to improper implantation, and increased risk of preterm birth.
Hence, treating thyroid conditions before trying to conceive can help reduce the likelihood of fertility issues. Fertility returns soon when hormone levels have returned to normal. The link between thyroid health and reproductive health isn’t exclusive to women. Thyroid disorders also influence male fertility; males with an underactive thyroid may have a poor libido and sperm count.
Dr Pandit and Dr Anitha B.R shares simple measures that will reduce the risk of thyroid-related problems with fertility:
- Quit smoking: It has been shown that smoking is harmful to thyroid health in both men and women; it is best avoided.
- Reducing soy consumption: It is best to consume soy in moderation and avoid it around the time of medication as it can interfere with your body’s absorption of Levo thyroxine
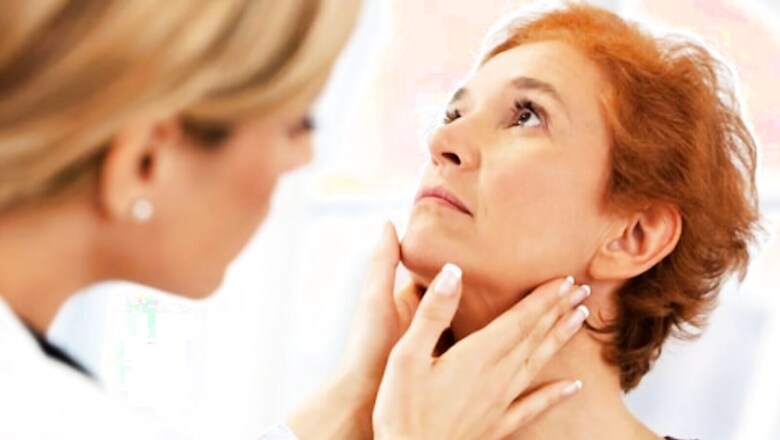
- Thyroid neck check: This is a method for detecting thyroid problems. This simple examination can identify swelling near the skin surface.
- Reduce stress: Include selenium-rich food like seafood, meat, eggs, bread, cereals, and grains as its deficiency can cause thyroiditis and Grave’s disease.
- Diet: Maintain a healthy diet and be physically active.
- Avoid outside food: Avoid artificial additives and processed foods.
- Limit intake: Less intake of vegetables like cabbage, cauliflower, and Broccoli.
Dr Pandit and Dr Anitha B.R explain lifestyle modifications that will benefit and reduce the risk of thyroid disease and fertility health.
- Early detection: Examining the thyroid gland in the neck is part of a thyroid check-up. It evaluates the neck for any potential enlargement and lump development, which may help out to diagnose the issues.
- Eliminate intense workouts; It is advised that anyone experiencing even minor thyroid symptoms refrain from engaging in any form of intense exercise. The thyroid patient needs to stay away from strenuous exercises like lengthy runs and bicycle trips.
- Consume Vital Vitamins and Nutrients; To combat thyroid-related issues, one must be mindful of diet consumption and aware of the nutritional value of each food item taken.
- Iodine: It is essential for the synthesis of thyroid hormone. It may end up being the most effective treatment for hypothyroidism sufferers. The regular salt we use in cooking contains iodine.
- Selenium: Try to eat foods high in selenium, such as eggs, almonds, tuna, etc. Selenium can be ingested in a respectable amount and is well known for its antioxidant qualities.
- Zinc: However, the normal person simply needs to absorb a proportionate amount of zinc from regular foods; taking zinc from external sources is rarely necessary. Foods containing zinc include whole grains, beef, lentils, seeds, nuts, dairy, eggs, and others.
Early diagnosis and identification are crucial in the fight against thyroid disorders, we must ensure that we have regular health screenings, cultivate good behaviors, and remove vices from our environment, such as excessive drinking, smoking, and unsaturated food products.
Read all the Latest Lifestyle News here



















Comments
0 comment