
views
- You may have blown a fuse if you experience sudden electrical failure with your radio, heating, windshield wipers, power outlets, or lighting systems.
- Use the fuse panel diagram to locate the correct fuse. You can also use a test light kit or multimeter tool to test for blown fuses.
- Use a pair of fuse pullers to remove the blown fuse. Replace the blown fuse with a new one of the same amperage.
Symptoms of a Blown Fuse

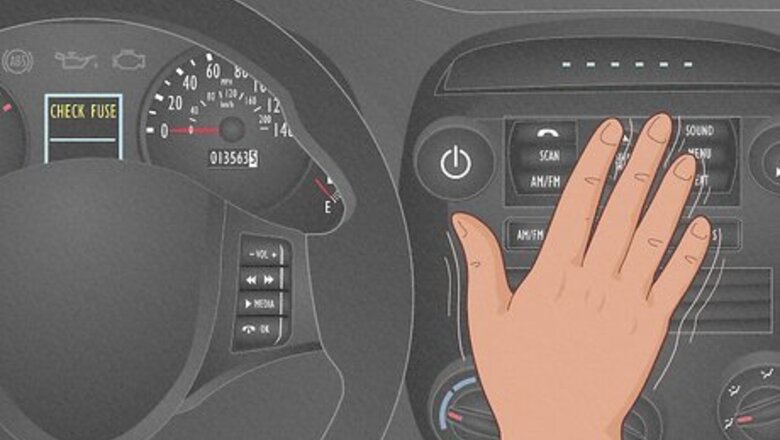
You experience sudden electrical failure inside your vehicle. One moment, your electronics are working, and in the next, you’re left with radio silence. A common experience for blown fuses is a sudden electrical failure. However, you may also note a slight burning smell from the fuse panel or see a “CHECK FUSE” light on your vehicle’s dashboard. Other common symptoms: Radio stops working Power door locks aren’t responding Heater fan or AC isn’t operating Power windows stop working Windshield wipers don’t move Power outlets aren’t functioning Headlights, taillights, and interior light systems don’t turn on
Locating the Blown Fuse

Keep your vehicle off and locate the fuse box. In some cases, vehicles may have two fuse boxes. The most common locations are the driver’s side of the dashboard, beneath the steering wheel, and beneath the hood. Remove the fuse panel’s cover to reveal different color-coded fuses with stamped amperage ratings. If you cannot locate your fuse box, it may also be placed near the front dash door or in the glove box. Refer to your vehicle’s owner manual for the exact location, as it may vary from vehicle to vehicle.

Identify the problem using the fuse diagram. In most vehicles, the fuse panel’s cover will have an intricate diagram of the fuse panel components, listing the locations and functions of each fuse panel. If you know you’re having an issue with your radio, search for a fuse labeled “radio.” For example, a blown 30A Fuse on a 2023 Ford F-150 indicates an issue with the fuel pump door. If your vehicle does not come equipped with a fuse diagram, go online and search for the year, make, and model of your car.
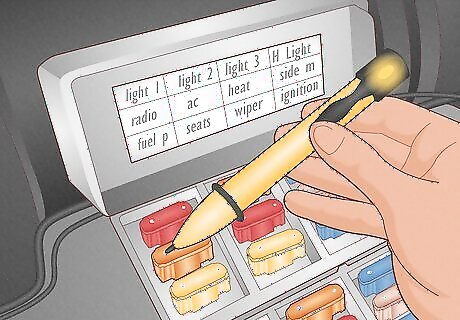
Alternatively, use a test light or multimeter to locate a blown fuse. Use a test light kit by attaching the clamp end of the test light to your vehicle’s negative battery terminal. Then, use the tool to tap the fuse’s pins on either side of the amperage rating.If the fuse is working, the pen will light on either side of the pins. If only one side light up, the fuse is blown. Use a multimeter tool to test multiple fuses. Set the multimeter to 20K ohms, which is a rating that refers to the restriction of power. Then, take the device’s protective tips off and touch both sides of the fuse. A good fuse will come up as 0.00. If you see a different number, the fuse is broken or damaged.

Remove the blown fuse with fuse pullers and inspect it for damage. Use a pair of fuse pullers to pull it out of its socket. Vehicles often come equipped with a fuse puller inside the box. If not, use tweezers or a similar tool to remove the fuse. Inside the transparent body of the fuse is one continuous metal strip, often U-shaped. Confirm the fuse is blown by checking for a split in the metal or burn marks. It can help to use a light source, like a flashlight or the light feature on your smartphone, to see the fuse clearly.
Replacing a Blown Fuse
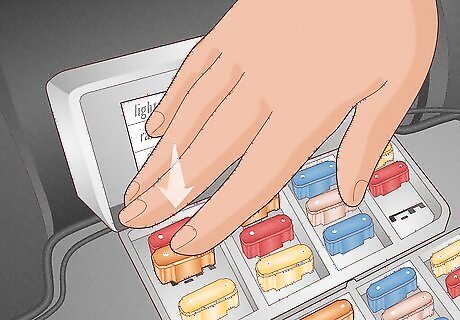
Replace the old fuse with an identical one. Use the same type of fuse and amperage rating when changing fuses in a car. This will prevent further short-circuits or additional damage to your car. Push it back into the correct slot using your finger or a fuse puller. Generally, many vehicles have additional fuses in the fuse panel. If you don’t have the fuse you need, visit your local auto shop or purchase one online.
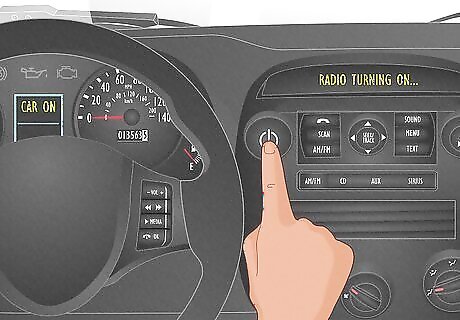
Test the circuit by powering your vehicle. Once the fuse has been replaced and the panel is covered, turn your vehicle on to see if the broken fuse is fixed. If working correctly, you should see immediate power to your vehicle’s radio, door locks, etc. If replacing the fuse doesn’t work, contact your local mechanic for a professional diagnosis.
What causes a car fuse to blow?

Faulty fuse replacement If your fuse continuously blows, make sure you’re using the correct amperage rating. A higher or lower-amperage-rated fuse can create frequent short circuits and cause extensive electrical damage to your vehicle. If you’re in a situation where you can’t quickly access the correct amperage, use a fuse from an unused component. For instance, if your vehicle’s radio and headlights share the same amperage, use the fuse from the radio as a temporary measure so you can see in the dark.
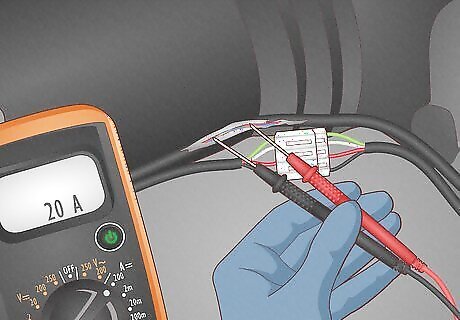
Shortages in the electrical system Short circuits result from a poor connection between the two conductors that supply electricity to your vehicle, often caused by internal damage. If this is the case, a professional mechanic will need to inspect the wiring and connection points to remedy the issue.
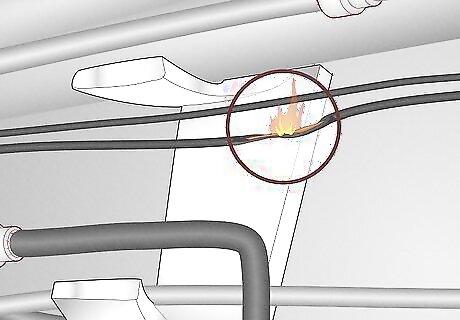
Wire insulation fraying As with any wires, their protectant shell may fray over time and use, exposing the wires to the vehicle’s metal frame and other surfaces. When this happens, it can cause short-circuiting and lead to an electrical fire.
















Comments
0 comment