
views
Identify the Objective, Method and Facts

Determine the main objective of the case study. You may be writing a case study to fulfill an academic requirement or to help solve problems in real-life situations. An academic assignment typically will come with a specific objective and instructions, whereas a professional assignment might require you to define the objective.
Select the best approach. Choose an analytical approach to increase awareness. In the preliminary stages of solving management problems, an analytical case study might best meet the goal of alerting upper management to core facts and issues. An analytical case study primarily focuses on what has occurred and why. Select a problem-solving approach to pinpoint and solve major issues. If the goal is to make solution recommendations, write a problem-solving case study that clearly outlines problems and solutions.

Conduct research for your case study. Examine the facts, dynamics, communications and all relevant aspects of the particular situation. Research might involve interviewing people in an organization, reviewing written documents or looking up relevant statistics.
Set the Scope for Readers

Explain the aim of the case study in the opening paragraph. The goal may be to understand the challenges of an organization or to solve interdepartmental conflicts.

Provide an industry or company overview. Certain facts or challenges may be common in the particular industry. For example, software bugs may be a common problem in the technology industry, requiring extensive product testing and quality control teams. Explain relevant factors to readers.

Outline relevant theories and knowledge. Case studies for academic programs typically require reference to theories and information presented in class. Refer to these theories and explain their relevance to solving the real-life issues in the case. For example, a theory may be that training employees in too large a group leads to less individualized attention and inadequate skills mastery.
Focus on Issues and Solutions

Identify all relevant issues. If many issues exist, focus on the most important ones. Some issues may be caused by underlying problems. For example, conflicts between team members may be due to unclear workplace policies or employee responsibilities.

Recommend solutions. List the most effective solutions first and explain how they will solve core issues. Address the challenges that might accompany suggested solutions. For example, cross-cultural conflicts in an organization might require additional training for managers, which may require funds or an extensive search for topic experts.
Provide a Clear Conclusion

Write a conclusion that summarizes the main issues and solutions. Emphasize the most effective recommendations.
Include a reference to relevant management theories. Explain in a few sentences how these theories support your conclusions.
Cite References

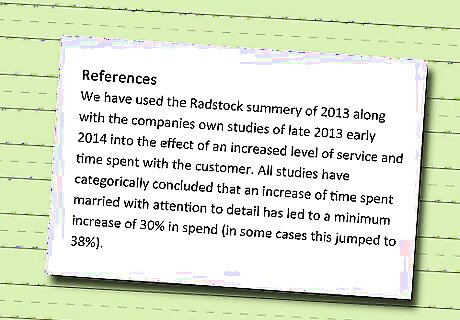
Include a list of references. Cite sources for all statistics, definitions, facts and other research.

Follow the required citation format. Check with your professor or manager, and/or review prior case studies in your workplace to identify the required citation format.




















Comments
0 comment