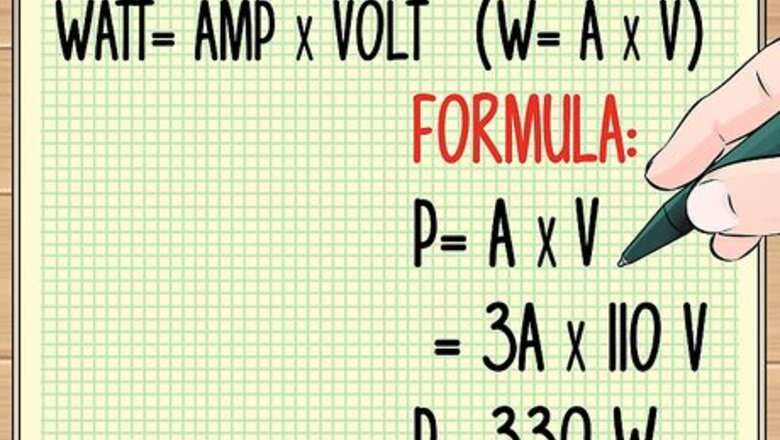
views
Using Math to Determine Watts
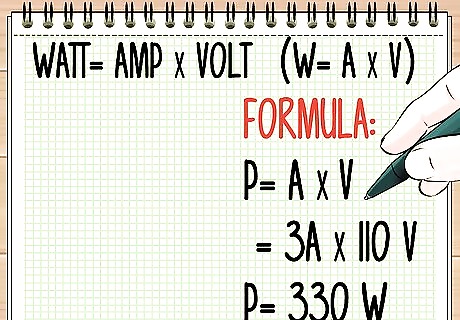
Determine the watts in a power source. You will need to know the amps and the volts in the power source. To determine the wattage, use a simple multiplication formula. The ampere (or amps) is the amount of electricity used. Voltage measures the force or pressure of the electricity. The number of watts is equal to amps multiplied by volts. That's it! In other words, watt=amp X volt. Sometimes you will see this formula written as W=A X V. For example, if the current is 3 amps (3A) and the voltage is 110V, you multiply 3 by 110, to get 330W (watts). The formula is P=3A X 110V = 330 W (with P standing for power). This is why watts are sometimes called volt-amps. Circuit breakers usually have the amps written on their handles. This is the maximum amperage that circuit can take before the circuit breaker trips. You can also determine both volts and amps by looking on the labels or in the operating manuals. You can look up common figures for standard appliances (most small appliances and lighting fixtures in homes require circuits that range from 15-20 amps and larger ones are 20 to 60. However, most counter top household appliances are rated for 120 volts and operated with 12 or less amps. Larger appliances like ranges and clothes dryers require more power and are connected to circuits that are wired to 240 volt power and may draw 20 to 40 amps depending on a number of factors. Household wiring is usually 120 or 240 volts in North America.

Determine amps or volts the same way. You can do the multiplication formula in reverse. For example, let’s say you have an AC 24-40 power supply. This means your power supply has 24 volts and 40 watts. The power source can supply 1.6 amps. The formula used is 40-? X 24. Thus, you would divide 40 by 24 to get 1.6. Here’s another reason you might need to do this. Let’s say you want to figure out the watts used by a ceiling fan, and the label on the fan says that the fan uses a certain number of amps. You could then find out the typical number of volts used by a ceiling fan (by calling the manufacturer or just looking online), multiply the two numbers, and generate an estimate of the wattage needed to run the ceiling fan.
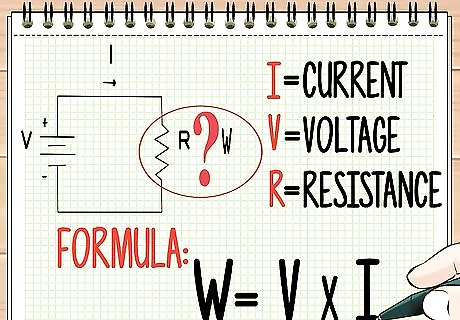
Determine resistor wattage. If you want to know wattage of a resistor, you will need to know the voltage (V) and the current (known as I). This is called Ohm’s law. The multiplication formula is voltage multiplied by current, expressed as W=V X I. Sometimes you will see the formula written with a P for power. The formula gets more complex when the power is changing over time. It involves using the time period to get the average. It’s hard to calculate, and for this kind of measurement, you should use special equipment known as a wattage meter.
Using Tools to Determine Wattage

Find an online calculator. There are many resources online that use calculators to determine watts. They will do the formula for you. Such resources typically ask you to enter the number of volts, and the number of amps. Then you are asked to hit the “calculate” button to get the watts. Keep in mind, though, that online calculators aren’t always accurate because every appliance is going to be slightly different in its power needs. Some online sites will give you the watts needed if you click on the appliance type, such as a television or desktop computer. Sites sometimes have charts that list the watts used by various appliances, from refrigerators to boom boxes.
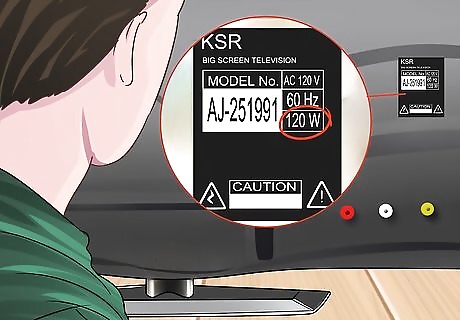
Check your appliance. You can figure out how many watts an appliance needs by looking for the data plate. Find this on the back of your appliance. It’s likely to list how many volts, amps, and watts you need to power your appliance. You might find this information stamped on the back of the appliance. Or you could find the wattage listed on the nameplate. Wattage meters plug into the appliance, and they tell you the exact amount of power that the appliance needs to run. The wattage of an appliance might vary depending on its setting. For example, a radio is going to use more watts if you turn the volume on high.
Learning More About Power Sources
Understand why watts matter. The power in watts is the rate at which energy is generated or used. Many utility companies will bill you based on how many watts of energy you used. The watt is basically how much energy an appliance uses. Rated watts are the amount of watts needed to keep an appliance running. For example, refrigerators usually require 500 watts to keep running. You may need to know the watts in your home if you are trying to become more energy efficient, add solar panels, or use a generator. Electrical power comes in AC and DC currents. AC means alternating current; the electrical current constantly reverses direction and is used often in homes and offices. DC means direct current, and it means the current only travels in one direction. You will find it in things like battery packs. Surge watts means the amount of watts needed to get an appliance started by igniting its motor or compressor. For example, it might take 2,000 watts to start the motor and compressor of a refrigerator.
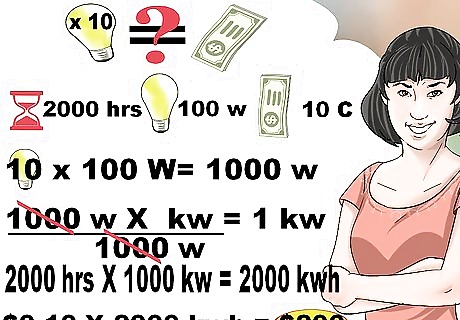
Become more energy efficient. Watts are a basic unit of power (electric, mechanical, or thermal). The reason watts matter is because you can improve energy efficiency if you understand them. Lower your watts, and you will improve energy efficiency and save money. Here’s an example. Let's say you are buying a light bulb, and one is 100 watts and the other is 23 watts. If the 100 Watt bulb is cheaper, you might assume it’s the better purchase. However, over time, the 23 Watt bulb will save you money. Do simple subtraction to determine the watt difference. In this case, that is 77 watts (100-23). Utility companies will often charge you using kilowatts. To find out the number of kilowatts, take the number of watts divided by 1,000. Then take the number of kilowatts multiplied by your hours of usage. This is the kilowatt/hr. Then, take kilowatt/hr and multiply that number by the cost of your energy. This is your annual cost. For example, let’s say you have 10 lights. They are each 100 watts. 10 X 100 = 1,000 watts. 1,000 Watts divided by 1,000 = 1 kW. Let’s say you’ve used 2,000 hours of energy. Thus, 1kW X 2,000 hours per year = 2,000 kwh. Let’s say your utility company charges you 10 cents for every kilowatt hour. You would take 2,000 kwh X .10 = $200, That's what it would cost you to use those bulbs for the year.
















Comments
0 comment