views
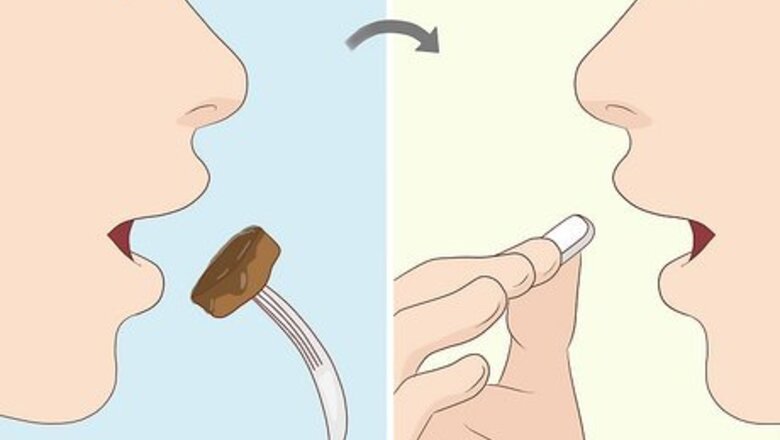
Should I take the supplement with food?
Yes, take vitamin D after the biggest meal of the day for ideal absorption. It doesn’t really matter if that’s dinner, lunch, or breakfast. Vitamin D is fat-soluble, which means it’s easier for your body to absorb it if there’s any kind of fat in your stomach to help it along. As a result, you’ll get the biggest benefit from your vitamin D if you take it immediately after eating. You will absorb the vitamin more efficiently if your meal contains a fat. You don’t need much fat, either. Any protein cooked in oil, or a small cup of yogurt will do the trick. Avocado, fish, olives, nuts, eggs, and cheese are all great sources of healthy fat!
What time of the day should I take my supplement?
Experiment to figure out what works best for you. Since vitamin D is fat soluble and it won’t make you sleepy or wake you up, you can take the supplement after any meal. Try taking it after breakfast, lunch, or dinner to see if there’s a particular time of day that works best for you. If the morning is easier, great! If it’s easier to take it after dinner, you can do that too. If you’re taking a regular vitamin, it may be easier for you to make it a habit by taking it at the same time every single day.
What else helps with the absorption of vitamin D?
Maintaining a healthy gut will help your body absorb vitamins. Your gut is responsible for breaking down vitamins, so making healthy decisions will help your body process vitamin D. Eat a healthy, balanced diet full of fruits and vegetables, and incorporate plenty of high-fiber foods in your meals. Get a good night’s sleep every night to avoid overworking your digestive track, and exercise regularly to keep your gut healthy and well regulated.
Keeping your liver and kidneys healthy will help with absorption as well. Your kidneys and liver help you break down vitamins, so keeping these organs healthy will help with vitamin D absorption. Aside from eating healthy and exercising, maintaining a healthy blood pressure will dramatically help maintain your kidney and liver function. On top of that, stop smoking if you’re an active smoker, and don’t drink more than 1 or 2 alcoholic beverages a day. In general, you shouldn’t consume more than 14 grams of pure alcohol a week. This translates to roughly 14 drinks.
What supplement dosage of vitamin D is too much?
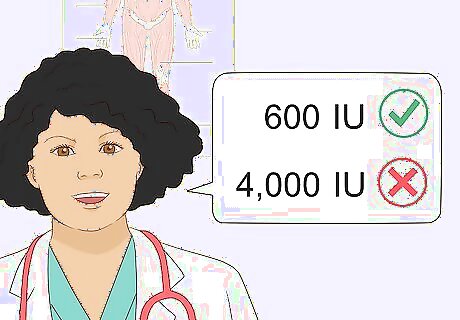
More than 4,000 IU is too much, and you only need 600 IU. The tolerable upper intake level for daily vitamin D consumption is 4,000 IU, and if you take more than that, you may start feeling a little queasy. However, that’s way more vitamin D than you need—most people only need 600 IU. Do not intentionally take more than 600 IU of vitamin D unless a doctor has advised you to do so. Adults over 70 years of age should take at least 800 IU. IU stands for international units; it’s the unit of measurement used to quantify vitamin amounts.
Signs of a vitamin D overdose include vomiting, weakness, and frequent urination. You may also experience pain in your bones and joints, and it can cause kidney issues. However, vitamin D overdoses are exceptionally rare, and you’d need to take 60,000 IU a day for several months for this to occur. You can’t overdose on vitamin D from sun exposure and foods.
Are vitamin D supplements effective?
Yes, supplements are a great way to get vitamin D if you can’t get sun. Most people get enough vitamin D from food and sunlight, with sunlight exposure being the bigger contributor. As a result, you do not need supplements in most cases. While your body will absorb vitamin D in basically any supplement form, vitamin D pills are likely the easiest and most efficient. If you’re worried about whether you’re getting enough vitamin D or not, ask your doctor to draw your blood and check your vitamin D levels.
Ask your doctor about taking supplements if you’re older or live far from the equator. Older adults tend to have more trouble getting enough vitamin D, and it can be tough to get enough sun if you live really far away from the equator—especially during the winter months when there’s less sunlight. If you suspect you need more vitamin D, talk to your doctor to get a screening test. You may not need additional vitamin D, but it’s possible you’d benefit from a daily supplement! If you do need a vitamin D supplement, it’s unlikely that you’ll need more than 600 IU a day. The scientific community is split on how many people genuinely need to take vitamin D supplements, since you can get a lot of it from food. So long as you aren’t taking more than 4,000 IU a day, there’s no serious downside to taking a supplement.
Is vitamin D2 or D3 better?
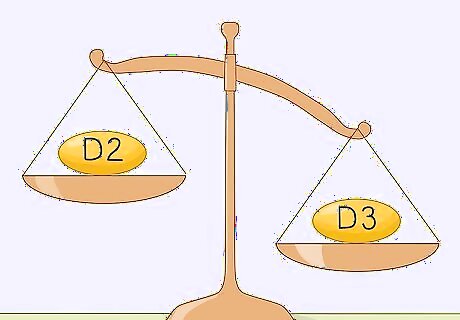
Vitamin D3 is more efficient, but D2 is good for you as well. Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) is produced in plants and fungi, while D3 (cholecalciferol) occurs naturally in mammals. Both forms are found in food and sunlight, and your body can use and store either of them. However, D3 tends to be a little cheaper, and it’s slightly more efficient in humans, so go for vitamin D3 if you’re buying supplements. This is one of those things where it’s probably not going to make a huge difference. D3 is slightly more potent, but it’s not like your body can’t utilize D2.
How does your body absorb vitamin D?
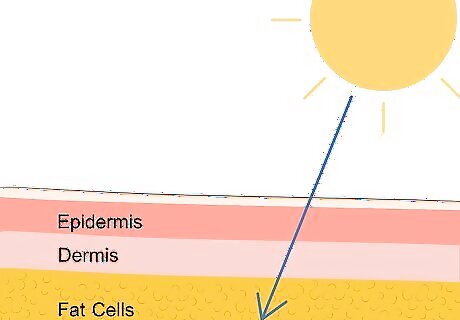
It comes in through your skin or stomach and stays in your fat cells. You can get vitamin D by exposing your skin to sunlight, eating food that contains vitamin D naturally, or taking a vitamin D supplement. Once the vitamin D enters your body, it is absorbed by the fat cells all over your body. It stays there until your body needs it to break down calcium in your intestines. The storage component is especially important here. Unless you aren’t getting enough vitamin D, the absorption rate and process isn’t particularly important; it’s going straight into storage regardless of how it’s absorbed. This is why staying indoors for a few days isn’t going to be a major problem.


















Comments
0 comment