views
Assessing the Situation
Survey the area. A stabbing often occurs during a volatile incident and the assailant(s) may still be in the vicinity, which could be dangerous for both you and the stabbing victim. Avoid making yourself a potential victim by intervening or going near the assailants. Only approach the victim once you have determined it is safe for you to do so. Although waiting until the assailants have left the scene does entail lost precious time for the stabbing victim, having more people injured is hardly conducive to rescuing anybody.

Call for emergency help immediately. If the person has been stabbed, it is critical to call emergency services as soon as possible. If you are the only person around, use your phone to call for help. If you don't have a phone with you, try to find a passersby or a nearby shop. You want to help the person as quickly as you can, but the most helpful thing you can do is get professional medical help for the victim as soon as possible. If the assailants are still nearby and you are unable to safely approach the victim, use that time to call emergency services.
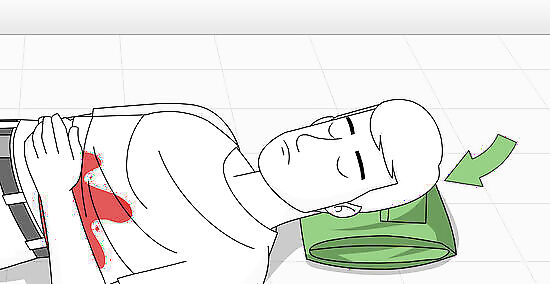
Lay the person down or get them to sit. Before you do anything else to attend to the stab wound, get the person to lie down on the ground. This will make it easier to help stabilize the victim, particularly if they start to get dizzy or fall unconscious. You don't want the person to risk aggravating the injury or harming themselves if they fall while fainting. For comfort, place a jacket or backpack under the victim's head. Alternatively, if there are other people around, ask one of them to sit with the person's head in their lap and talk to them. This will be soothing to the victim and help them keep calm.
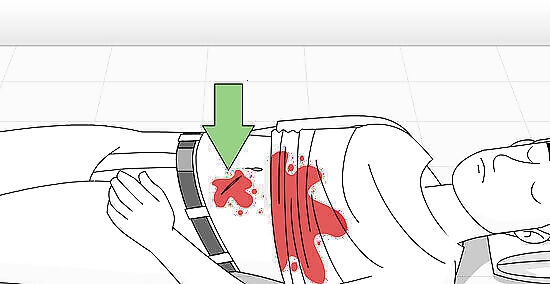
Examine the person and determine the extent of the injury. Is there something stuck in the wound? Is there more than one stab wound? Are there slashes? Where is the blood coming from? Is it on the front or back of the body? You will probably have to part the person's clothing to properly identify the wound(s). Try to look for and identify all wounds before starting your treatment. However, if you notice one obviously severe wound that needs urgent treatment, deal with it immediately. A severe wound would be one that is bleeding steadily and profusely or one that is spurting out blood like a geyser. Spurting blood is usually a sign that the wound has hit an artery.
Attending to the Stab Wound
Put on disposable gloves if you have them. Alternatively, put some plastic bags over your hands. Though this step is not required in order to tend to the stab wound, it is important in order to protect yourself, so as to reduce the risk of infection to you or the victim. If available, nitrile or other non-latex gloves are preferable. These types of gloves minimize the possibility of an allergic reaction to latex, which can complicate treatment. Nitrile and other non-latex gloves are usually blue or purple and are rapidly replacing the white latex gloves that were previously the standard. If you don't have gloves with you, try to wash your hands or even use a hand sanitizer quickly. If you have nothing available to you, try to use layers of cloth to keep a barrier between yourself and the victim's blood. Remember, you do not have to touch the person if you believe that you are in danger of contracting an infection or are otherwise uncomfortable. Wait for emergency assistance if you are in doubt. If you choose to treat the victim, do your best to minimize contact with the victim's blood.
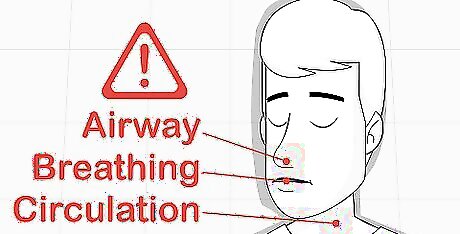
Check the victim's ABCs, Airway, Breathing, and Circulation. Make sure the person's airway remains unobstructed. Listen for the sound of breathing and watch the person's chest for movement. Check the victim's pulse to make sure the heart is still beating. If the victim has stopped breathing, perform CPR. If the person is conscious, begin working but also talk with them to keep them calm and help slow their heart rate. If possible, try to keep the victim's eyes averted so they cannot see the wound.
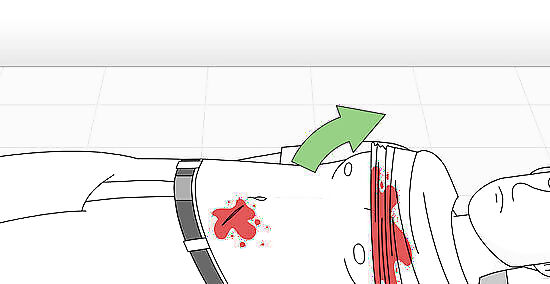
Remove the victim's clothing around the affected area. This will enable you to identify the precise location of the stab wound and then apply treatment. Stab wounds can sometimes be obscured by clothing, blood, other fluids, and even dirt or mud, depending on where the victim is found. Use care in removing the victim's clothing since they are likely in considerable pain.
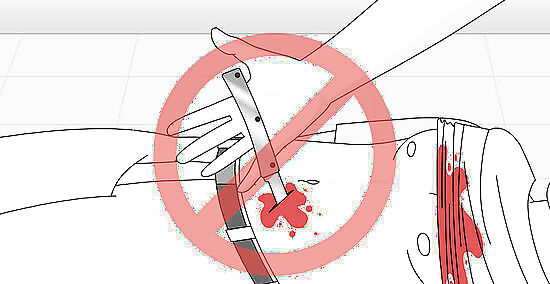
Refrain from removing the stabbing object if it is embedded. Leave the object in the wound if it is still there and be very careful not to move it, which may cause further damage. The object is actually helping to stem the blood flow. Pulling it out will likely increase blood loss, while pushing it in may cause further injury to the internal organs. You'll need to apply pressure and dress the wound around the object as best you can. Medical professionals will be better able to remove the object without damaging any internal organs or causing massive blood loss in the process.
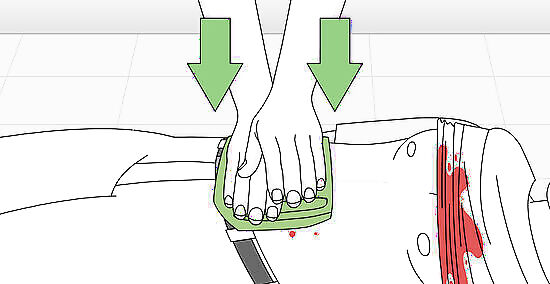
Stop the bleeding. Apply pressure on the wound with a clean and absorbent material (like a shirt or towel), or preferably, a clean dressing such as sterile gauze. If the object is still in the wound, press firmly around it. Applying pressure to the wound will help to slow the flow of blood. If the wound is bleeding profusely, apply pressure to the major artery leading to the area with your hand, while your other hand continues to apply pressure on the wound. These areas are called "pressure points.” For example, to slow bleeding in the arm, press the inside of the arm just above the elbow or just below the armpit. If the wound is on the leg, press just behind the knee or in the groin.
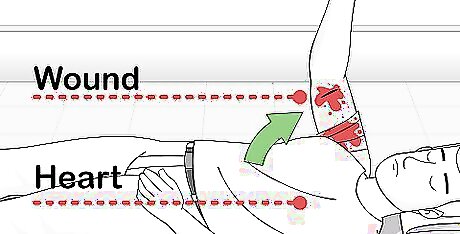
Reposition the victim so the wound is above the heart. This will help slow down blood loss. Keep in mind, though, that applying pressure to the wound needs to be a higher priority than elevating it.
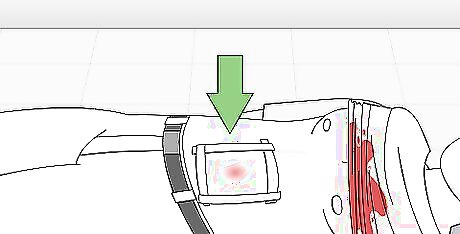
Cover the wound with a dressing. If you happen to have first aid materials with you, fasten the dressing in place using a bandage or tape. Do not lift or remove the dressing as this will disrupt clot formation and re-start the bleeding. If the dressing becomes soaked with blood, add more cloth material on top of it. If you don't have any materials to fasten the dressing in place, simply continue to apply pressure. This will help the blood clot. Only use a tourniquet if applying pressure doesn’t help stop the bleeding. It’s important to know how and when to use a tourniquet—if a tourniquet is applied incorrectly, it may lead to an unnecessary serious injury to or loss of the affected limb.
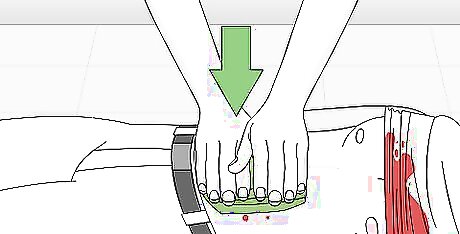
Continue to apply pressure to the wound until help arrives. While waiting for emergency help, continue to monitor the ABCs: airway, breathing, and circulation. Look for and treat symptoms of shock. Symptoms of shock include cool, clammy skin, paleness, rapid pulse or breathing, nausea or vomiting, dizziness or fainting, and increased anxiety or agitation. If you suspect the victim may be in shock, loosen any tight clothing and cover them with a blanket to warm them. Try to get the victim to stay still. See how to treat shock for details.
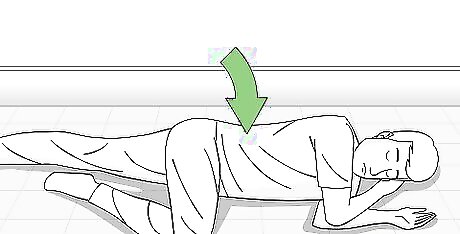
Check the victim's consciousness. If the victim falls unconscious, you'll need to act quickly. Place the victim in the recovery position, on their side with the head tilted back and the hand further away from the ground under the head and the arm closest to the ground either bent or straight out. The leg further away from the ground (the top leg) should be bent for stability and to keep the victim from rolling forward. Do not put someone in the recovery position if you suspect they have a spinal or neck injury. Monitor the person's breathing. If the unconscious victim stops breathing, place the victim on their back and perform CPR.
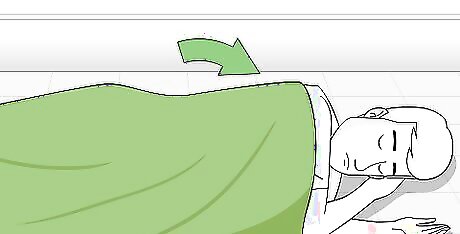
Keep the victim warm and comfortable. Both shock and loss of blood can cause the victim to suffer from lowered body temperature. Throw a blanket, coat, or some other warm item over the victim to keep them warm. Keep the victim as still as possible. Whether lying or sitting down, the person should be kept still and calm. It is important that someone remains with the person constantly to both reassure them and to monitor their condition.
Cleaning and Closing a Stab Wound
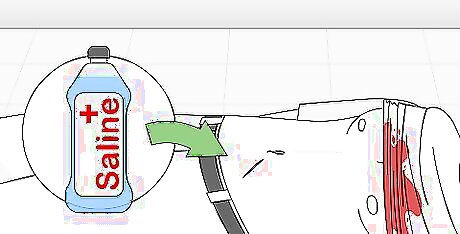
Begin cleaning the wound. If you are isolated and not able to call emergency services (e.g., if you are camping or in the wilderness), you should clean the wound once you have some control over the bleeding. In normal circumstances, this would be the job of emergency personnel, but there may be times when you need to do this yourself. Remove any debris from the wound if present. Keep in mind, however, that even a wound without debris has had an object jabbed in it and there's no way of knowing how clean that item was. In other words, every wound should be cleaned properly. It’s best to irrigate the wound with running water first. Then, dip a bandage in saline and dab around the wound to clean it. Once the wound is clean, dry it off with a clean cloth. The victim will likely experience pain when the wound is being cleaned so if the person is conscious, give them a warning.
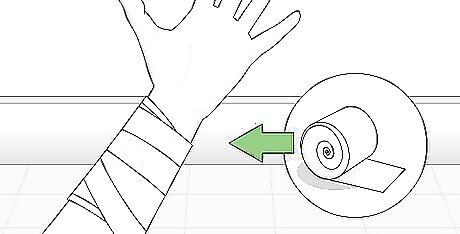
Pack the wound. A dirty wound should not be closed, and any stabbing is considered dirty. Packing the wound should help to avoid any contamination from outside materials, like dirt, which could cause an infection. Stab wounds should be packed with gauze and covered with a dressing and tape. In this case, you are covering the wound, not binding it, as you wait for it to clot. Ask your doctor how often the wound needs to be repacked. If a wound will not cease bleeding, do NOT close it.
Apply antibiotic treatment, if available. If you have any antibiotic ointment, apply it to the wound whenever you replace the dressing. This will also help avoid any infection from setting in.
Check that the bandage is not too tight. Check the area furthest away from the heart for each limb that has a bandage on it. For example, if the person has an arm wound, examine their fingers. If the person has a leg wound, check their toes. If a bandage is too tight, it may cut off blood flow to the area below it, which is dangerous and can permanently damage the tissue. You can tell if this is happening because these areas will become discolored (blue or dark-colored). Loosen the bandage if you notice this happening and seek emergency assistance as soon as possible.














Comments
0 comment