views
- If your car won’t start after filling up with gas, the most likely issue is a stuck EVAP purge valve. It could also be an issue with the fuel filter or fuel pump.
- If your "Check Engine" light comes on, use an OBD-II scanner to read the code and diagnose the issue.
- If you're not comfortable making the repairs yourself, have your car towed to an auto shop so a mechanic can fix the problem.
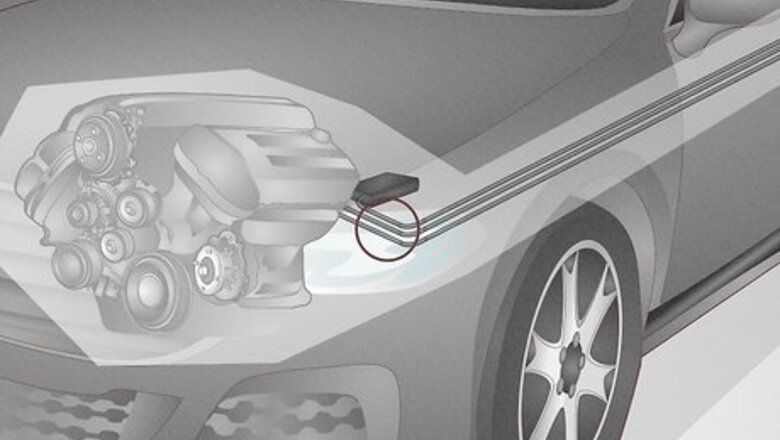
Stuck EVAP Purge Control Valve
The EVAP (Evaporative Emission Control) system prevents gasoline vapors from escaping into the atmosphere from the fuel system. The purge valve operates using a solenoid, which can sometimes malfunction, causing the valve to stay closed. Signs: If the purge control valve isn’t working properly, the engine might rough or stall out, the engine might smell like gasoline, the car might not accelerate smoothly, and the Check Engine light may be illuminated. How to test: If your car’s engine light pops on, use an OBD-II code scanner to read your car’s codes and make sure that the valve is the cause of the issue. How to fix: Bring your car to a mechanic and have them inspect and replace the valve. Estimated Replacement Cost: $160-183.
Bad Gas

Your car might not start if the gasoline can’t combust as it should. This can happen if you accidentally put diesel in your tank, or if the gasoline has gone through phase separation, which can happen if the gasoline sits for a long time or if it absorbs too much water from the atmosphere. Signs: If your car has been filled with “bad” gas, it might idle roughly, have stalling issues, make pinging sounds, or force the Check Engine light to come on. How to fix: Call a tow truck and have them bring your car to a mechanic. If you put diesel in your tank, you will need to have them drain the tank, flush the fuel system, and fill it back up with fresh fuel. If it’s “bad” gas, the best solution is to have your tank pumped out and filled with fresh gas. Prevention: Make sure you always visit a reputable gas station, and if you think you’ve received bad fuel, don’t visit that station again. Also, check your owner’s manual to see what kind of fuel you should use. Estimated Repair Cost: $50-200
Clogged Fuel Filter

Your fuel filter strains out contaminants from gasoline before it reaches the engine. When the filter becomes full of dirt, salt, and other debris from transported gas, it could restrict fuel flow to the engine. Signs: Before your car stopped starting, you may have experienced less power when you’re accelerating or pulling a load, the check engine light might’ve been on, the engine stumbled or stalled while driving or idling, the fuel pump quit, you consumed more fuel per mile, and the engine might have fired up for a second but then died again. How to fix: If your fuel filter is grimy enough to stop your vehicle from starting, replace it yourself or visit a mechanic. Some vehicles don’t have a replaceable fuel pump—instead, they have a screen on their fuel pump, so you may need to have the pump serviced. Prevention: Consult your owner's manual to find out how long your fuel filter will last before it needs to be replaced. If your car is older, you may need to have your fuel filter replaced every 1 ½ to 2 years, or about every 20,000 to 30,000 miles. Estimated Replacement Cost: $50-175.
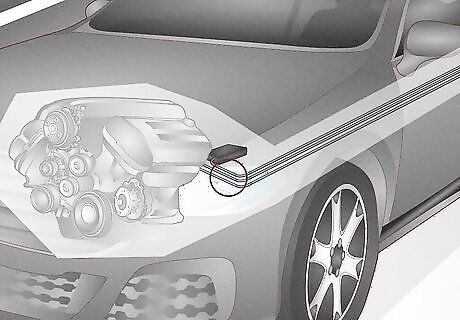
Clogged Charcoal Canister
The charcoal canister is used to capture gas vapors and draw them into the engine, where they can be burned to generate power. It’s best to replace the canister as soon as possible to avoid breathing in gas fumes. Signs: If the charcoal canister is congested or broken, you might notice a strong gas smell coming from your engine, your check engine light may be illuminated, your vehicle might not drive as far as it normally would on a full tank, and you may hear a hissing noise coming from your fuel tank whenever you fill up with gas. How to fix: Hire a mechanic to replace the charcoal canister. Prevention: The charcoal canister can go bad if you repeatedly fill your gas tank to the brim or overfill it, which can saturate the charcoal with gasoline. It can also become damaged or dislodged if you bottom out your vehicle. Only fill your gas tank until the pump kicks off and try to avoid driving over anything that might damage the underside of your vehicle. Estimated Replacement Cost: $440-500.
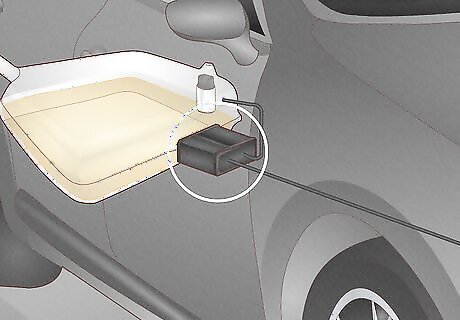
Bad Fuel Pump
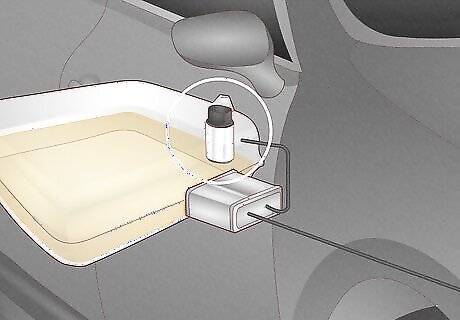
The fuel pump delivers gas to the engine through fuel lines and can go bad if debris passes through the filter into the tank, blocking the flow of fuel and causing the pump to overheat. Your fuel pump can also fail if the oxygen sensor is faulty, or when the pump has experienced years of general wear and tear. Signs: Your fuel pump might be the issue if your car has stuttered and stumbled when nothing else seems wrong, you heard whining from the pump, the car had difficulty accelerating, or if the car cut off or slowed down for no reason while driving. How to test: Before replacing your pump, replace the filter first to see if that’s the issue. You can also use a fuel pressure test kit to check the fuel pump. If your fuel-injected car doesn’t have a psi of 40 or more, you may have to get it replaced. How to fix: Bring your car to a mechanic to have them replace the fuel pump. Prevention: In general, you should replace your fuel pump every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, but if the pump overheats you might have to replace it more frequently. To keep it from overheating, keep your gas tank filled up before you reach empty. Estimated Replacement Cost: $75-250.
Corroded Battery Terminals
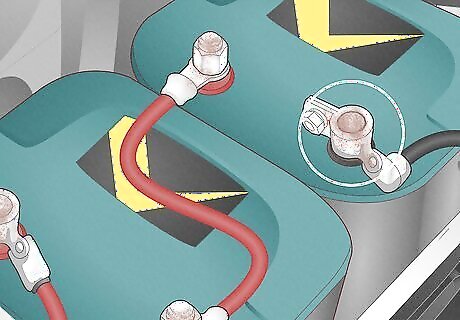
Corrosion builds up on battery terminals when hydrogen gas is released from sulfuric acid inside the battery. Before cleaning corrosion, put on protective gloves and eyewear and remove anything that could ignite away from the area. Signs: Check for corrosion before assuming the battery is dead. Corrosion can be caused by overcharging the battery, contact with copper clamps, or because the battery is nearing the end of its lifespan. If the battery is cracked or damaged, get your entire battery replaced right away. How to test: Push your car at least 20 feet (6.1 meters) away from the gas station. Inspect underneath the battery covers for a white, blue, or green crust. If corrosion is present, carefully remove the negative clamp, then the positive clamp. How to fix: Clean the corroded terminals using a battery-cleaning solution or a baking soda paste made of 3 tbs (1.5 oz) of baking soda and 1 tbs (0.5 oz) of distilled water. Rinse the solution with a spray bottle or wet cloth, then connect the positive clamp before the negative clamp. Start your vehicle to see if that solved the issue—if it didn’t, your battery may be dead. Prevention: Inspect the battery every 6 months for corrosion. To help prevent corrosion in the future, remove the battery cables and apply a protective treatment or petroleum jelly after inspecting. Estimated Repair Cost: $15
Dead Battery

If your car’s battery stopped working, it may need to be replaced. If your battery is cracked, damaged, or leaking, it’s important to have a mechanic look at it right away. Signs: If your car doesn’t turn over, it could be that the battery is dead. If your car’s lights have seemed dim or you have been having trouble with the radio, windshield wipers, and other electronic devices on your car, it could mean that your battery was weak and needed to be replaced soon. How to test: If your car’s battery isn’t completely dead, you may be able to jumpstart it and give it enough charge to go get it replaced. Push your car away from the gas station fuel pumps and use another vehicle or a jump box tojumpstart your car. How to fix: If your vehicle doesn’t jumpstart after a couple of tries, call a tow truck and have your car brought to a mechanic or replace the battery yourself. If you have a dead battery, it’s a good idea to ask to have the alternator checked to make sure you don’t have to have it serviced as well. Prevention: Batteries typically last around 4-6 years—at the 4-year mark, pay attention to the signs that your battery is weak, listed above. Ask a mechanic or a service technician to see how much charge it has when you go in for regular maintenance. Estimated Replacement Cost: $45-250
Failing Alternator

The alternator converts energy into electricity that is used to power the car’s electrical systems and recharge the battery. Your alternator is made up of many parts that are susceptible to wear and tear, and if you notice it failing, get it looked at by a professional immediately to avoid more costly repairs. Signs: If your alternator is starting to fail, you might notice the “ALT,” “GEN” or battery-shaped warning light illuminate, your headlights may dim or flicker, you hear grinding or whining sounds, smell burnt rubber or electrical fire, your radio or electric windows are starting to fail, or your car stalls frequently, the alternator may be the issue. How to fix: Bring your car to a mechanic right away if your car shows any of these symptoms. Prevention: There are tons of things that could cause your alternator to fail, and not all of them can be avoided. However, making sure that your car undergoes regular maintenance, refraining from using the radio or other electronic devices with the car engine off, and avoiding leaving the car stopped for a long time can help conserve the life of your alternator. Estimated Replacement Cost: $740-850
Starter Malfunction

Your starter is a small motor that gets your engine up and running. If your car won’t start, it could be caused by a defective starter motor, relay, or another part of the ignition system. Signs: If the dashboard warning lights come on when you try to start your car, you hear a clicking noise when you try to turn the key, your engine cranks over very slowly, you see smoke, or if you see an oil leak when you pop the hood, your starter might need to be replaced. How to test: Try jumpstarting your battery. If the battery and the battery cables are in working order, try lightly tapping the starter with a hard object to try and get the electrical components back in contact with each other. How to fix: If jumpstarting or tapping doesn’t fix the issue, call a tow truck and get your car to a mechanic to have the starter repaired or replaced. It’s best to have a professional look at your starter to prevent damaging the rest of the system. Prevention: There are many things that could cause a starter to go bad, including loose wiring, dirty or corroded connections, battery corrosion, damaged or worn-out parts, oil leaks that drip onto the starter, or a bad relay fuse. Have your vehicle inspected and serviced regularly. Estimated Replacement Cost: $730-820
Spark Issues
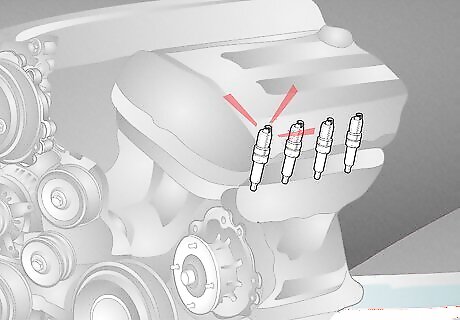
The ignition system sparks the engine to get the car moving. If the spark plugs aren’t the issue, it may be the spark plug wires, the ignition module, the circuit, or the switch. Signs: If your spark plugs are going bad, you may notice that your vehicle struggles to start in cold weather or after sitting for a few hours, your vehicle cranks for a long time before starting, your car makes rattling noises and vibrates excessively, your car struggles to accelerate, your engine misfires, the check engine light illuminates, or the car’s exhaust system smells like gas. How to fix: Take your car to a mechanic and have them look at the ignition system and replace the spark plugs if necessary. Prevention: Check your owner’s manual to see how often your spark plugs should be replaced to help avoid issues in the future. Most manufacturers generally recommend replacing them every 30,000 miles. Estimated Replacement Cost: $3-25 per spark plug












Comments
0 comment