
views
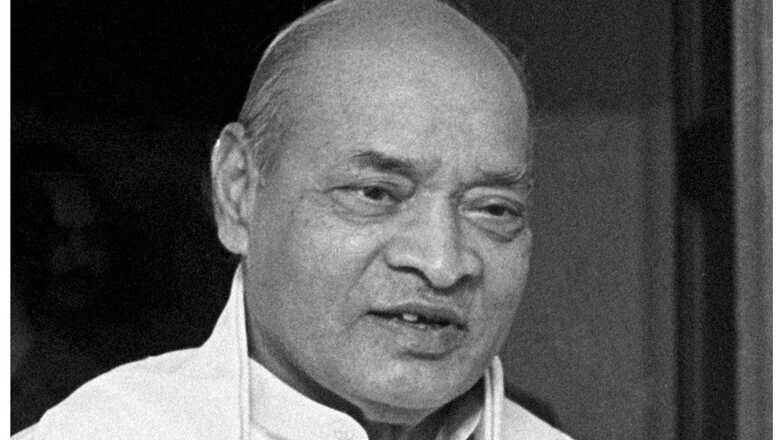
Former prime minister P V Narasimha Rao will be honoured with the Bharat Ratna, Prime Minister Narendra Modi said on Friday. He said Rao’s visionary leadership was instrumental in making India economically advanced and laid a solid foundation for its prosperity and growth. Know about India’s historic economic reforms of 1991 that were undertaken under the prime ministership of Rao.
“Narasimha Rao Garu’s tenure as Prime Minister was marked by significant measures that opened India to global markets, fostering a new era of economic development,” Prime Minister Narendra Modi said in a post on X.
Delighted to share that our former Prime Minister, Shri PV Narasimha Rao Garu, will be honoured with the Bharat Ratna.As a distinguished scholar and statesman, Narasimha Rao Garu served India extensively in various capacities. He is equally remembered for the work he did as… pic.twitter.com/lihdk2BzDU
— Narendra Modi (@narendramodi) February 9, 2024
Why Were The Economic Reforms Brought In 1991?
The economic reforms of 1991 were triggered by the economic woes during the period, during which the country faced the balance of payment (BoP) crisis where its forex reserves were able to cover only 15 days of imports.
What Led To The BoP Crisis of 1991?
Fiscal Deficit: The country’s fiscal deficit during 1990-91 reached as high as 8.4 per cent of GDP. The fiscal deficit is the difference between the total expenditure and revenue of the government. It is an indication of the total borrowings that are needed by the government.
Gulf War I: In 1990-91, the domestic economic situation was further aggravated by the geopolitical crisis in West Asia. The prices of crude oil surged due to Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait.
High Inflation: India’s inflation during the period also rose sharply. It accelerated from 6.7 per cent to 16.7 per cent due to a rapid increase in money supply, thus making the country’s economic situation worse.
The 1991 Reforms
In order to get the country out of this deep economic mess of 1991, former prime minister Manmohan Singh, who was the then finance minister, launched India’s biggest economic reforms under the prime ministership of P V Narasimha Rao. The historic reforms to open up the economy were based on the LPG model — liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation.
Liberalisation: Under this, industrial Licence Raj was abolished. Only a few hazardous industries, like chemicals, now required a licence. Except for those, every other industry could be set up without any licence. Commercial banks were allowed to decide on interest rates, etc.
Privatisation: Under this, banking reforms were brought in. Markets were de-regularised. Private sectors were introduced. PSU shares were allowed to be sold to private entities.
Globalisation: Import duties were reduced. The Indian rupee became partly convertible. All capital and intermediate goods were released from the import constraints list. The economy was opened up for international trade and foreign investment.















Comments
0 comment