views
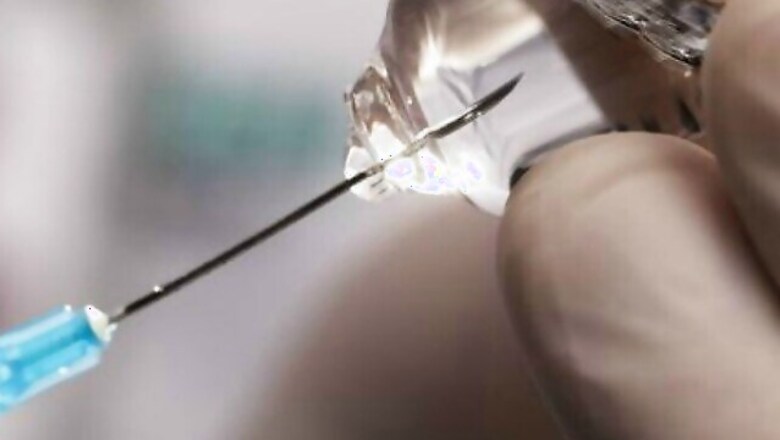
Tokyo: Scientists have developed a novel capsule made from seaweed extract for preserving insulin-producing pancreatic cells, offering hope to diabetic patients to lead a needle-free life.
Patients with type 1 diabetes require daily insulin injections. Pancreatic islet transplantation is an effective treatment that can dramatically reduce daily doses or even eliminate dependence on external insulin, researchers said. So far only human islets can be transplanted and their supply is low. Cryopreservation, or deep freezing, is the method commonly used for the islet preservation and transportation.
However, the freezing process poses a challenge. As the cells are cooled, water in and around them freezes. Ice crystals have sharp edges that can pierce membranes and compromise cell viability. Researchers led by Amy Shen, head from Okinawa Institute of Technology and Science Graduate University (OIST) in Japan developed a novel cryopreservation method that helps to protect pancreatic islets from ice damage. The novel technique employs a droplet microfluidic device to encapsulate pancreatic islets in hydrogel made of alginate, a natural polymer extracted from seaweed.
These capsules have a unique microstructure - a porous network and considerable amount of non-freezable water. There are three types of water in the hydrogel: Free water, which is regular water, freezes at 0 degree Celsius, producing ice crystals, Freezable bound water also crystallises, but the freezing point is lower, Non-freezable bound water does not form ice due to the strong association between water molecules and the hydrogel networks.
Hydrogel capsules with large amounts of non-freezable bound water protect the cells from the ice damage.
Islet encapsulation reduces the risk of rejection of transplanted cells by the recipient. The hydrogel capsule allows small molecules, eg nutrients and islet secretions, to pass through the membrane easily, but prevents direct contact between implanted islets and host
cells.
Encapsulation also may prevent an attack on transplants by the autoimmune response that destroyed the patient's own islets in the first place. The microencapsulation method can help to overcome some major challenges in pancreatic islet transplantation, including the scarcity of available islets and the lack of simple and reliable control methods, especially for individual islet assessment.
It offers hope to patients suffering from type 1 diabetes to return to a "normal" life, free of insulin injections. The study was published in the journal Advanced Healthcare Materials.















Comments
0 comment