
views
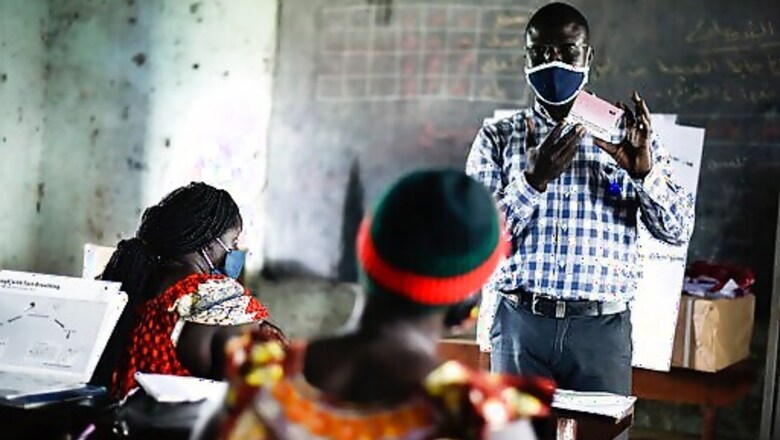
JOHANNESBURG: The coronavirus is exposing an uncomfortable inequality in the billion-dollar system that delivers life-saving aid for countries in crisis: Most money that flows from the U.S. and other donors goes to international aid groups instead of local ones. Now local aid workers are exposed on the pandemic’s front lines with painfully few means to help the vulnerable communities they know so well.
Often lacking protective equipment, the groups are carrying a bigger burden than ever as COVID-19 adds to the already vast challenges of conflict, drought and hunger in places like Afghanistan and Somalia.
At times, they tell communities they have nothing to give.
Our hands are tied, a South Sudanese aid leader, Gloriah Soma, told an online event last month. She described foreign aid workers being evacuated early in the pandemic or working from home as many feared infection.
Is this a humanitarian response? she asked, saying she hopes the crisis will spark more help at this critical moment. Her country can hardly bear another disaster: A five-year civil war killed nearly 400,000 people, and hunger stalks half the population.
The world’s most precarious regions are long accustomed to the sight of international aid organizations, often managed by expats. Now some of those foreign workers are questioning their roles amid the reckoning over racial injustice in the U.S. and elsewhere.
At times criticized as white saviors, some say local partners should be given more responsibility and money. A local group can do more with it, Soma said. She asserted that $100,000 could help over 10,000 people, while the same amount to an international group will only pay one or two staff, “and thats it.
Recognizing the problem, major global donors including the U.S., Germany and Japan and humanitarian groups had pledged to give at least one-quarter of international aid money to local partners as directly as possible by this year. But just over 2% reached them directly last year, according to a report by the U.K.-based Development Initiatives last month.
COVID is a horrible tragedy, but its going to force us to work differently, the United Nations humanitarian agencys director of humanitarian financing, Lisa Carty, has said. U.N. leaders are discussing how to make sure money moves more quickly to frontline responders.
One-quarter of the $1 billion allocated by U.N. country-based funds went to local aid organizations last year, Carty said, but I think we all agree that we want to do better.
And those funds manage just a small fraction of overall aid money. Most goes to U.N. agencies, while local aid groups are often seen as subcontractors of those agencies and international organizations. Tracking where the money goes remains a challenge.
Now some pandemic-hit donor countries are reducing humanitarian aid meaning even less money is trickling down to people on the front lines.
In Somalia, where the al-Qaida-linked al-Shabab extremist group remains a deadly threat, local aid groups are able to reach and deliver aid in places where access is difficult. Unfortunately, very little COVID-19 funding has been directly allocated” to them,” said Amy Croome, Oxfam’s communications manager there.
In South Sudan, a survey of 19 local organizations found 58% had lost at least half their funding because of the pandemic.
Many are ill-prepared for COVID-19.
People believe the disease is widespread across the country, but theres very limited testing capacity, said Jeff Okello, who leads The Health Support Organization in South Sudan. The group’s limited supply of personal protective equipment is left over from the recent Ebola outbreak in neighboring eastern Congo, he said.
Most parts of South Sudan are reached only by local organizations, he said. Now the pandemic has worsened everything. I think we have over 30 letters written by different communities across the country asking us to help them, Okello said. His response: If we get the resources, we will come.
He pointed out that international aid groups have the benefit of medical evacuation if workers get infected, while local aid groups must survive on their own.
Several other South Sudanese local aid leaders said they’ve cut staff or restricted work in communities where theyre often the only source of help.
We always say Thank God for the little we get, but its not what we used to get, said James Keah, who leads UNIDO South Sudan.
His group received $400,000 this year from the U.N.s South Sudan Humanitarian Fund for health services. With few other means of substantial support, some 100 field staffers have left and services in several regions have stopped.
Local communities are told, You just have to cope with it,” Keah said.
Moses Poloya with Health Link South Sudan said his group received about $400,000 less than last year. It now struggles to serve more than 1 million people at over 100 health centers, some lacking protective gear.
He believes donors think local aid partners arent ready to handle larger amounts of money, a source of frustration. Groups like his are resilient and always present, he said.
The U.N. humanitarian agency said nearly half, or 44%, of the $34 million in the South Sudan Humanitarian Fund has gone to local organizations this year. Forty-four such groups received money, down from 120 last year, reflecting changes meant to make projects more sustainable.
But with the unprecedented global crisis, the U.N. said it and others simply do not have enough to meet the growing humanitarian needs.
More than 300 local aid groups are registered in South Sudan, meaning nearly all must scramble for support, said Angelina Nyajima. Her Hope Restoration group has added the production of face masks and soap to its women-focused services to meet soaring demand.
Groups like hers are at a disadvantage because international aid groups have the backing of richer home countries, she said. “For us, we have no mother country. South Sudans government limps along two years after its civil war ended, with humanitarian groups providing most basic services.
But Nyajima said COVID-19 is forcing donors to take notice as South Sudanese find ways to serve desperate communities on very little.
I think its high time, with the corona incident, she said. It has shown exactly what the locals can do.
Disclaimer: This post has been auto-published from an agency feed without any modifications to the text and has not been reviewed by an editor

















Comments
0 comment