
views
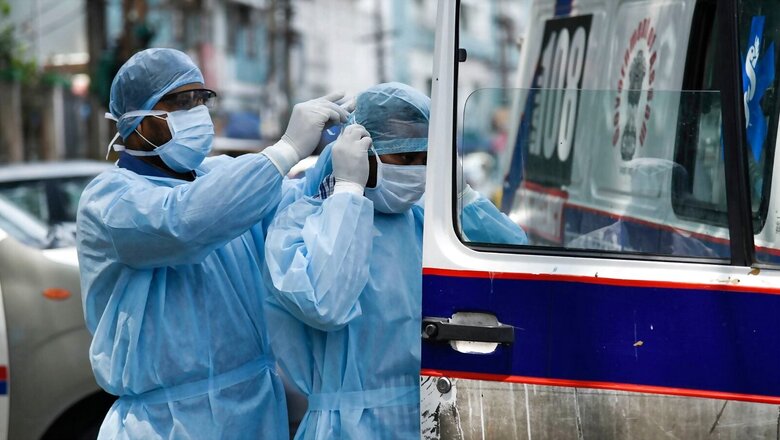
The World Bank hailed India’s efforts in tackling Covid-19 pandemic in a report documenting the challenges, innovations and lessons in the procurement of essential medical items. In a paper titled, ‘India Covid-19 Procurement: Challenges, innovations, and Lessons’, shared by the health ministry on Tuesday, the World Bank noted that the Indian government’s decision to have centralised procurement, support to long-term market development and production of Emergency Medical Equipment (EME) and early export restrictions worked in its favour during the public health emergency in the country.
“Covid-19 created unprecedented shortages of essential medical supplies and equipment due to the sudden surge in demand,” the paper said according to a report by the Hindustan Times. “Severe global supply chain constraints of essential Covid commodities and unprecedented demand for lifesaving equipment led to an entirely supplier-driven market and a huge variation in prices.”
As per the report, the creation of empowered inter-ministerial groups helped the government to make prompt decisions for a centralised procurement to support the states. “Flexible conditions were permitted under the existing legal frameworks and budgets to undertake fast-track procurement, while empowered groups helped to accelerate decision making. Initially, this enabled accelerated imports, and over time, the development of local markets, based on a whole-of-government approach,” it said.
The World Bank and the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) jointly funded the ‘Covid-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Strengthening Project’ worth $1.5 billion (Rs 11,983.5 crore).
According to its assessment, the World Bank listed four key innovations by India that helped in successful handling of the pandemic situation in the country, according to the HT report. These included: the adoption of a whole-of-government approach to stimulate local production that helped to steeply reduce unit prices and dependency on global supplies; introduction of accelerated tendering process and quality assurance protocols; efficient supply chain management informed by computerized modeling to project cases and admissions for oxygen, intensive care unit requirements based on epidemiological trends; and quick quality-assured Covid commodities to the government’s e-procurement site for prompt access to these products at competitive prices without going through a tendering process.
The report praised India for not compromising the quality of essential commodities during the large-scale procurement project. It hailed India’s central procurement agency, HLL Lifecare Limited, for hiring inspection agencies to undertake pre-dispatch inspections at manufacturing sites to ensure quality products. In February 2020, HLL was picked as the central agency to accelerate emergency procurement of essential medical commodities during the Covid-19 pandemic.
The quality assessment was then independently conducted by competent laboratories such as DRDO, Defense Research Development Establishment (DRDE), Aerial Delivery Research and Development Establishment (ADRDE), Labs of Ordinance Factory Board, South India Textile Research Association (SITRA).
“Initially, the rejections, mostly due to poor penetration at seams of PPE, were as high as 20–30 per cent, but the product quality improved significantly later. SITRA also developed a Blood Penetration Resistance Tester for PPE and licensed a company to produce and make this equipment available to the industry to help internal quality control,” stated the report, reported Livemint.
The World Bank also noted that the Indian government provided a conducive environment for the growth of the indigenous medical devices industry. At the beginning of the pandemic, India was mostly importing ventilators but 25 manufacturers including several newcomers came forward to produce ventilators with limited financial and infrastructure capacity, it said.
The government made use of several automobile and electrical manufacturing companies to handhold these new entrepreneurs to produce ventilators.
Read all the Latest News India and Breaking News here
















Comments
0 comment