
views
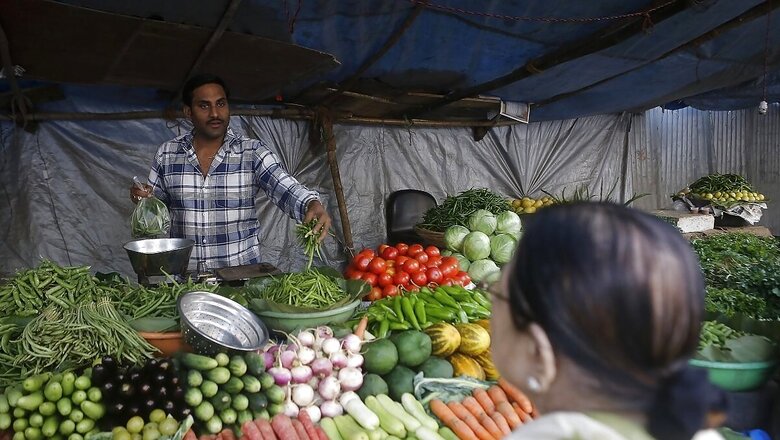
The prices of tomatoes have skyrocketed in the Indian markets. As per reports, Delhi, Bengaluru, and Uttar Pradesh are among the states that are seeing a Rs 100 to Rs 120 per kg price in the retail market, and in many other places, the price of tomatoes has gone up to Rs 70 per kg. What is the reason behind this sudden surge in prices? The price rise is due to factors such as heatwave, delayed rainfall, and lack of interest among farmers to grow the crop amid crashing prices in early May. Moreover, wholesale dealers attributed the price rise to heavy rainfall in various regions of north India which resulted in damage to the crop thereby limiting its availability.
Just like tomatoes, all the products in the market are impacted by supply and demand. Demand and supply are one of the most integral aspects of economics. It is important to understand these terms not only for examination point of view but also for practical knowledge. Supply and demand are fundamental economic concepts. The two describe how changes in the price of a commodity, product, or resource impact its supply and demand. Demand and supply are dependent on people, processes, and technology.
Let us understand these terminologies individually and the relationship between the two in Classes With News18.
What is Demand?
Demand is the consumer’s desire for a good or service. Consumers are interested in purchasing that product for a particular price. Demand can increase or decrease based on several factors. The demand curve is defined as the relationship between the price of the good and the amount or quantity the consumer is willing and able to purchase in a specified time period, given constant levels of the other determinants–tastes, income, prices of related goods, expectations, and the number of buyers.
Law of Demand- When there is a rise in the price of a commodity, the customer demands less quantity. Whereas, when the prices of the commodity fall, the demand for the commodity will rise.
Factors Impacting Demand-
1. Price of the product
2. Income of Consumers
3. Availability of Alternatives
4. Number of Consumers
5. Consumer Expectation
What is Supply?
Supply represents the capability or willingness of a seller to provide a particular good/service in the market. To ensure this, companies have a dedicated logistics and supply chain department. In general, supply is based on the demand and price of a product. Higher the price, the greater the incentive for the firm to sell more.
Law of Supply- The law of supply implies that when there is an increase in the price of the commodity, the quantity of the commodity produced and available for sale also increases. On the other hand, when the price of the commodity drops, the supply also decreases. This occurs because of the fact that the higher the price, the higher will be the profit margin.
Factors Impacting Supply:
1. Product Prices
2. Availability of Raw Material
3. Producer’s Expectations
4. Costs of Input
Relationship Between Supply and Demand
– When the supply of any product increases, the price of that product will decrease, and demand will rise due to low prices.
– If the demand for a product is too high, the supply will be short in the market. This will, in turn, increase the prices of that product. However, with exorbitant prices, the demand will fall since people will not want to pay such high prices. In turn, the price will have to be decreased to sell that product or service.
Equilibrium Point
The equilibrium point is a situation wherein the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of a commodity intersect. This represents the equilibrium price. It is the point at which both the buyers and the sellers are satisfied. Equilibrium is also called the market-clearing price or market equilibrium.
















Comments
0 comment