
views
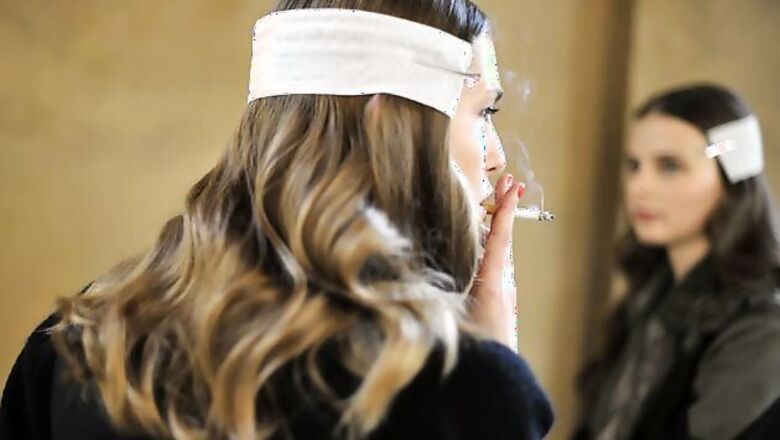
Washington: It's known that women find it a bit harder to kick the butt than men. Now, a new study has found why - it's because their brains respond quite differently to nicotine than male smokers. When a person smokes, the number of nicotine receptors in the brain - which bind to nicotine and reinforce the habit of smoking - are thought to increase in number.
Researchers at the Yale University School of Medicine in the US found this is true in men - male smokers had a greater number of nicotine receptors compared to nonsmokers. But surprisingly, women smokers had about the same number of nicotine receptors as nonsmokers, they found.
"When you look at it by gender, you see this big difference," study author Kelly Cosgrove, an assistant professor of psychiatry, was quoted as saying by LiveScience.
The findings suggest that elements of smoking not related to nicotine, such as the smell and act of holding a cigarette, may play a greater role in fuelling the habit of women smokers compared with men, Cosgrove said.
The results are important because the main treatments for people who want to quit smoking are nicotine-replacement therapies, such as nicotine patches and gums, he said.
The study, published in the April issue of Archives of General Psychiatry, suggests women smokers may benefit more from other types of treatment that don't involve nicotine, including behavioural therapies, such as exercise or relaxation techniques, and non-nicotine containing medications, he added.
In the study, Cosgrove and colleagues scanned the brains of 52 men and 58 women, about half of whom were smokers. They examined nicotine receptors in brain by using a radioactive marker that binds specifically to receptors that are primarily responsible for the body's physical dependence on nicotine.
Smokers in the study had abstained from smoking for a week so that their nicotine receptors would be free to bind to the marker used for imaging.
The researchers found that male smokers had about 16 per cent more nicotine receptors in an area of their brain known as the striatum, 17 per cent more in the cerebellum, and 13 to 17 per cent more in the cortical region, or outside layer, of the brain compared with male nonsmokers.
Female smokers, on the other hand, had similar numbers of nicotine receptors in these regions as in male nonsmokers.
Dr Len Horovitz, a pulmonary specialist at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York, agreed more attention should be paid to non-nicotine related smoking therapies.
"You can replace all the nicotine you want, and people might still want to smoke," Horovitz said.
For instance, smoking is a big stress reliever for some people. Even the act of deep breathing is a part of the habit, and breathing exercises may help smokers because they mimic puffing a cigarette, Horovitz said.
The reason for the sex difference seen in the study is not known, but it may have something to do with levels of the hormone progesterone.
Levels of this hormone fluctuate in females depending on the stage of the menstrual cycle, and are much higher after ovulation. The study found higher levels of progesterone were associated with a lower number of available nicotine receptors, the researchers said, suggesting progesterone may indirectly block these receptors.

















Comments
0 comment