views
- DOS is an old operating system that was used by PCs before Windows.
- DOS is a text-based operating system that does not have a graphical interface.
- The Windows Command Prompt still uses DOS commands, but it is not DOS
Open the Command Prompt (Windows only). If you're on a computer with DOS as the operating system, the command prompt should appear automatically when you boot up the computer. If you're using a Windows computer, you'll need to start the Windows Command Prompt. To do so, click the Windows Start button and type cmd. Then click Command Prompt. You should see a window with "C:\>", "C:\DOCUMENTS AND SETTINGS\[your name]>", or something similar. This is called the "command prompt." The letter at the beginning of the command prompt (i.e. "C:\") tells you what drive letter you are in. The text after the drive letter tells you what directory or folder you are in. For access to more commands, hidden files, the ability to add and delete users, change user passwords, and more administrative abilities, you'll need to run the Command Prompt as an administrator. If you are having technical issues with Windows, you can boot your computer into the Command Prompt. This allows you to run your computer just using a command line, which is more efficient than the Windows graphical user interface. You can run programs more quickly and efficiently, as well as delete programs infected with viruses and malware.

List the contents of a directory or folder. To do so, type dir and press Enter. This lists the contents of the directory or folder you are in. The most important thing you should be able to do is to list the contents of directories and navigate them. Files are listed by file size, followed by the file name (i.e, "countdown.txt"). Directories and folders will have the tag "

Navigate to another directory. To do so, type cd followed by a directory name and press Enter. For example, if you wanted to change to the "Games" directory, you would type cd games and press Enter If the directory is in another directory, you would separate each subdirectory name with a "\". For example, if you want to navigate to a folder called "Mortar" within the "Games" directory, you would type cd games\mortar and press Enter. You can also specify the full path of the directory you want to navigate to (i.e, cd c:\games\mortar. If the directory has spaces in the title, you need to put the name of the directory in quotation marks. For example cd "mortar mayhem". To go back to the previous directory. type cd.. and press Enter. To return to the root of your hard drive, simply type cd\ and press Enter. This will return you to "C:\>."
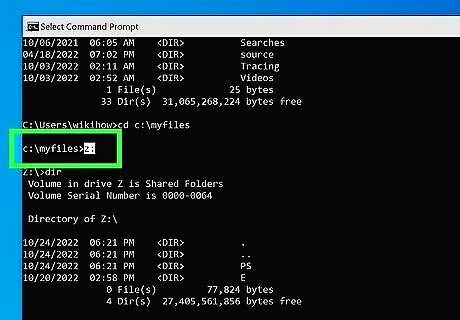
Change to a different drive letter. If you want to want to change to another drive, such as a D: drive, a CD/DVD ROM, a flash drive, or another external device, simply type the drive letter followed by a colon (":") and press Enter. For example, type D: and press Enter to change to the D: drive. You can do this from within any directory. You can also format, and partition a drive using the DOS or the Command Prompt.
Type the name of a program or file name to run the program or file. Executing programs is exactly like commands. For example, if you wanted to start the game Mortar Mayhem, you would navigate to the directory it's in, type mortar.exe, and press Enter. You can do the same thing using batch files and other scripts. If the file name or program has spaces in the title, you need to put the file name in quotation marks. Running programs from within DOS or the Command Prompt allows you to use switches and flags that allow you to do specific things with a program, rather than just running an executable file. For example, if you design a level for the original DOOM 2 (a ".wad" file), you would navigate to the folder that contains your WAD file and the DOOM2.exe file. Then you would type doom2.exe -file filename.wad and press Enter to launch DOOM 2 with your custom level. If you want to be able to run a program from any folder or directory within the Command Prompt, you need to add the program to your PATH environment variable.
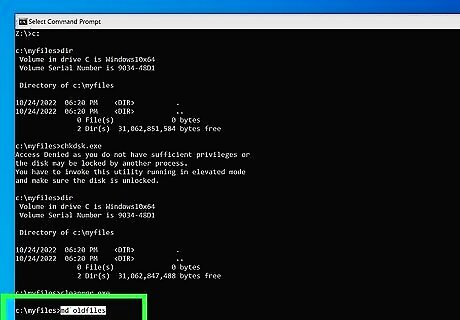
Create a new directory or folder. To do so, navigate to the directory or folder you want to create the new directory in, and type mkdir or md followed by the name of the directory and press Enter. For example,mkdir new_directory You can create multiple directories using this command. Simply separate each directory name with a space. For example, md user1 user2 user3. If you want the new directory name to have spaces, you need to put the directory name in quotation marks. For example, mkdir "My New Directory".
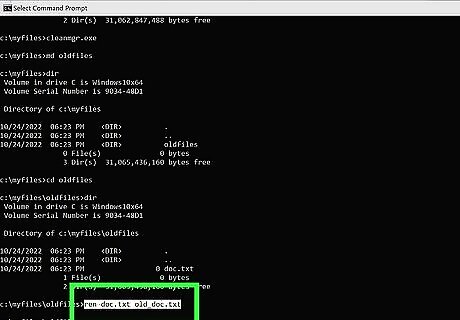
Rename a file. To do so, navigate to the directory or folder with the file you want to rename Then type ren followed by the name of the file you want to rename, followed by the file name you want to rename it to. For example, type ren count.txt coundown.txt to rename a file called "count.txt" to "countdown.txt." If you are not currently in the directory with the file you want to rename, you will need to specify the path to that file. For example, type ren c:\documents to specify that the "count.txt" file is in the "documents" directory.

Delete a file. To do so, navigate to the folder with the file you want to delete, and type del followed by a filename and press Enter. For example, type del countdown.txt to delete a file called "countdown.txt." If you want to delete all files within your current directory, type del *.* and press Enter. Be careful when using the "del" command. Once a file is deleted in DOS, you cannot get it back.

Copy a file to another folder. To do so, navigate to the folder with the file you want to copy. Then type copy followed by the file you want to copy. Then enter the full path you want to copy the file to and press Enter. For example, type copy countdown.txt c:\games\grape to move the "countdown.txt" file to the "grape" folder within the "games directory. If you want to copy an entire directory along with all the subdirectories contained within, type robocopy followed by the path to the directory name, followed by the path you want to copy it to, and press Enter. For example, you could type robocopy c:\games\grape c:\documents to copy the "grape" folder to the "documents" folder.

Move a file to another folder. To do so, navigate to the file you want to move. Then type move followed by the file you want to move, and then the full path or the directory you want to move it to. For example, type move countdown.txt c:\games\grape to move "countdown.txt" to the "grape" directory within the "games" directory. If you are not currently in the same directory as the file you want to move, you will need to specify the path to the file in the command. For example, type c:\documents\countdown.txt c:\games\grape to move the "countdown.txt" file from the "documents" folder to the "grape" directory within "games."
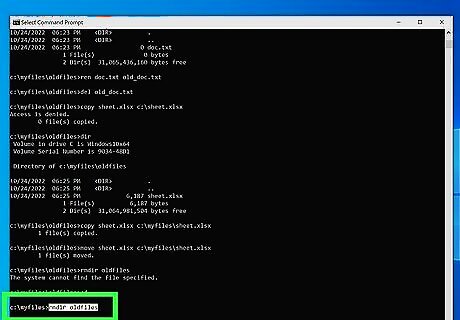
Delete a directory. If you want to remove an entire directory, type rmdir followed by the directory name and press Enter. Be careful when using this command, this will delete an entire directory and all its contents. Once it is deleted, there is no way to get it back.
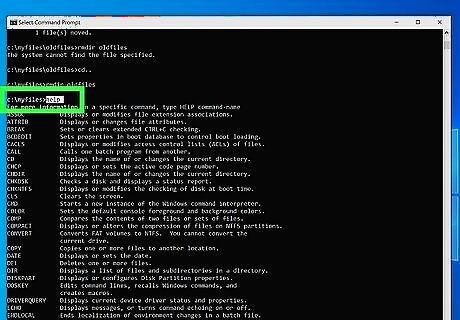
View a complete list of commands. If you want to view a complete list of commands, simply type help and press Enter. This will display all the commands you can use in DOS. If you are uncertain what a command does, simply type the command followed by "/?." This will give you information about the command, and how to use it.

















Comments
0 comment