
views
X
Research source
Taking Cephalexin

Follow your doctor's instructions for taking Cephalexin. Do not take larger or smaller amounts of the drug, and do not take it for any longer than what the doctor has prescribed. Make sure that you carefully read the instructions on the prescription label before you begin taking the drug.

Drink water with your Cephalexin capsules or tablets. Cephalexin capsules or tablets should be taken with a full glass of water. Other drinks may affect the effectiveness of the drug. If you are taking the capsule or tablet form, do not chew or try to dissolve it in your mouth. It should be swallowed whole along with the water.
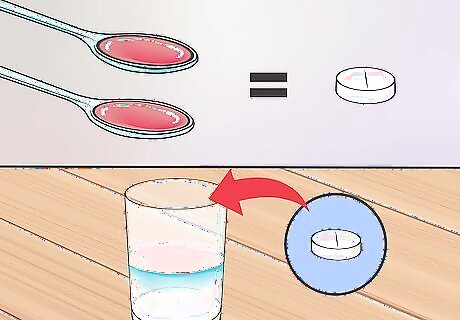
Use water to dissolve tablets if taking the dissolvable form of Cephalexin. When using the dissolvable tablet, never chew or swallow the tablet. Dissolvable tablets are designed to be combined with liquid before taking the medicine so that the medicine will be metabolized faster by the body. Dissolve the drug in 2 teaspoons of water. Stir the mixture until it is fully dissolved. Drink the solution immediately. To ensure that you have taken the entire dose, add water to the glass and swirl gently to collect remaining drug, then drink the water.
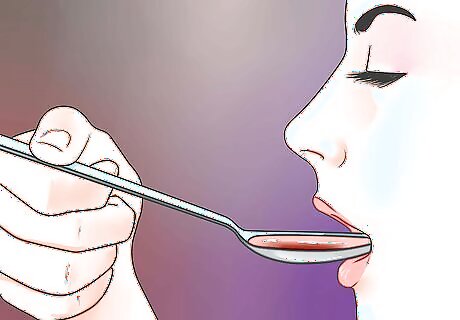
Take liquid Cephalexin as directed by your doctor. Follow your doctor's instructions for taking liquid Cephalexin. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have questions. If you are using the oral suspension liquid form of Cephalexin, you will need to shake the container before use. It is also crucial that you take the correct dose by using a measuring cup or spoon. Often the dose is given in milliliters (ml), so a medicine syringe (without a needle) is commonly used to measure the dose. If you do not have a measuring device, ask a pharmacist for one.
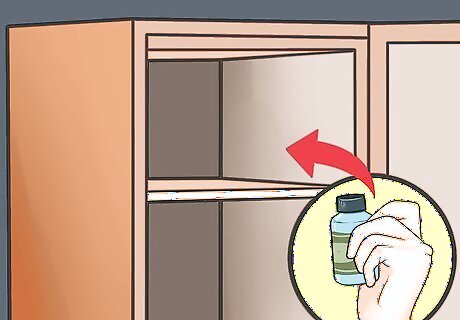
Store Cephalexin in a cool, dry place. Remaining Cephalexin drugs should be stored properly. Store the drug in a cool, dry place with temperatures not exceeding 86 degrees Fahrenheit (30 degrees Celsius). Do not store this drug in the bathroom because the moisture may affect the quality of the tablets or capsules. Liquid Cephalexin should be stored in the refrigerator. Do not freeze this medication. Throw away any unused medicine after 14 days.

Have some food or a glass of milk when you take Cephalexin. Cephalexin may cause an upset stomach if taken without food. To prevent an upset stomach, take Cephalexin with a meal, a snack, or at least a glass of milk. If you still experience an upset stomach when taking Cephalexin with food or if the upset stomach is severe, talk to your doctor about it.

Take any missed doses of Cephalexin as soon as you remember. However, if there is 1 to 2 hours left for the next dose, just skip the missed dose altogether and wait for the next scheduled time. Never try to take double dose just to make up for the missed dose. This may lead to overdose and adverse side effects.
Understanding Cephalexin
Understand that Cephalexin is used to combat bacteria within the body. This drug is known as bactericidal, which means that its primary mode of action is to inhibit or disrupt the bacteria's cell wall and cause it to burst or rupture. Cephalexin is effective against some gram positive and gram negative bacteria. These bacteria include bacillus, corynebacterium, clostridium, listeria, staphylococcus and streptococcus. Cephalexin does not exhibit any therapeutic effect on viral infection. It is also not used to treat methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Take Cephalexin to combat bacterial infection. Cephalexin is primarily used against bacterial infection. Bacterial infections may include bone and joint infections, pneumonia, skin, urinary tract and middle ear infection. In some cases, Cephalexin serves as a prophylactic drug - meaning, it is used to prevent certain infections. For example, this drug is used to prevent bacterial endocarditis.

Be aware that improper use of Cephalexin may reduce its effectiveness. Taking Cephalexin when you do not have a bacterial infection may reduce the effectiveness of antibiotics when you really need them. Cephalexin may also be less effective if you do not take the full dose or cycle that your doctor has prescribed. Talk to your doctor if you still have symptoms of infection after taking all of your medication.
Talking to Your Doctor About Cephalexin

Tell your doctor about any allergies that you have. Do not use Cephalexin if you are allergic to it. In most cases, if you have a known allergy to Cephalexin, you probably will also be allergic to other cephalosporin antibiotics. Some of the examples of cephalosporin are cefaclor, cefadroxil, cefdinir, cefditoren, cefixime, cefprozil, ceftazidime, and cefuroxime. If you notice, cephalosporin drugs start with 'cef'. Remember this and you will be better prepared to avoid this drug. Also tell your doctor if you are allergic to penicillin or amoxicillin. You may have a higher chance of being allergic to cephalexin.

Make sure your doctor is aware of any underlying conditions you have. You should not take Cephalexin if you have certain underlying conditions. Some medical conditions or diseases may also stop you from taking Cephalexin. These diseases may include kidney and liver disease, colitis, diabetes and malnutrition. Most of these diseases alter your body's ability to metabolize Cephalexin. For example, Cephalexin contains sugar, so you might not want to take it if you have diabetes.

Inform your doctor if you are pregnant. There have not been many studies about the effects of Cephalexin on unborn babies. Therefore, it is best to discuss alternative options with your physician if you are pregnant. Cephalexin should only be taken by pregnant women if there is no other choice.

Make your doctor aware of any other medications you're currently taking. If you are taking any other drugs aside from Cephalexin, let your doctor know about it. There is a chance for drug interaction – meaning taking another drug may affect the effectiveness of Cephalexin. For example, some vaccines that contain bacteria such as typhoid and BCG may be affected by Cephalexin. In addition, some studies show that Cephalexin can interfere with the effectiveness of oral contraceptives. So if you are taking Cephalexin while taking pills, you might get pregnant. Other drugs that may interact with Cephalexin are Coumadin, metformin and probenecid.

Tell your doctor if you are taking any herbal medicines. Certain herbal medicines may interfere with the effectiveness of Cephalexin, so it's important to inform your doctor of any herbal medicines or supplements that you are currently taking.

Let your doctor know if you don't think Cephalexin is a good choice for you. If you feel like there is a reason that you shouldn't take Cephalexin, it's a good idea to tell your doctor. Your doctor may either reduce the dose or switch you to a different drug entirely. Special tests, such as a skin test, can also be done to determine if you can safely take the drug.
Knowing When to See Your Doctor
Talk to your doctor before taking the drug. It is crucial to talk to your doctor before taking the drug. Your doctor will be able to give you comprehensive and accurate instructions pertaining to the proper use of the medication. Never attempt to self-prescribe Cephalexin or take someone else's medication.
Notify your doctor if you experience any severe or persistent side effects. Cephalexin has some common side effects, that should be mild and short-lived. If these side effects become unmanageable or severe, notify your doctor. These side effects include: upset stomach diarrhea vomiting mild skin rashes

See your doctor immediately if you experience any serious side effects or symptoms of a possible allergic reaction. When taking Cephalexin, you should call your doctor right away if you experience any serious side effects. You or your doctor may file a report with the Food and Drug Administration's (FDA) MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program online at http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch or by phone at 1-800-332-1088. These serious side effects that you should watch for include: difficulty breathing or swallowing unusual bleeding and bruising sore throat vaginal infection wheezing hives severe skin rash itching painful mouth and throat sores diarrhea that is severe, or with blood or mucus dark colored or decreased urine fever pale or yellow skin















Comments
0 comment