
views
Preparing the Habitat
Choose the right type of enclosure. Your baby tortoise needs a habitat, but not just anything will do. Glass aquariums, which many people use, are actually not very good habitats for tortoises because the sides are too high and there is often not enough floor space. Tortoises also do not understand glass and can run into it. A wider, shallower container will work much better. A large plastic storage container works well for an indoor habitat. (No top is needed.) When you need a larger container, you can build or purchase a tortoise table, which is a large wooden enclosure on tall legs.
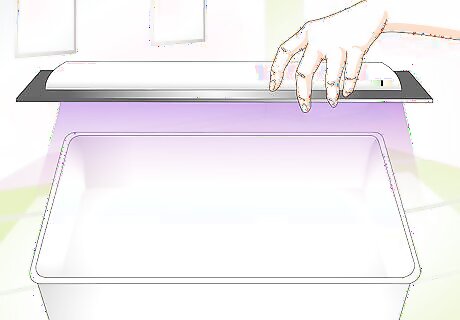
Ensure proper UV exposure. In the wild, tortoises bask in the sun to regulate their body temperatures and absorb vitamin D. To keep your tortoise healthy, it's important to simulate this exposure in captivity. Letting your tortoise out to bask in the natural sunlight for a few hours a week is a good idea. Do not put a glass tank in direct sunlight, however, as this can cause the enclosed area to become too hot. When your tortoise does not have access to natural sunlight, use a UV lamp to provide artificial sunlight. The exact amount of UV exposure your tortoise will require depends on the species, but it varies between 8 and 12 hours per day.
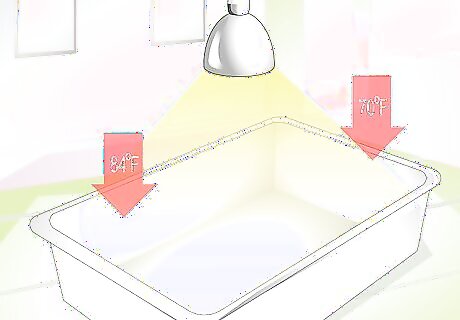
Make sure the habitat is the correct heat and humidity. All tortoises need to live in warm habitats. It's a good idea to use heating lamps to create a gradient temperature within the enclosure. One side should be 22°C (70°F), and the other should be 29°C (84°F). The proper humidity level will depend on the species you have, so make sure you properly identify it. Desert tortoises should be kept in dry habitats, while tropical tortoises should be kept in moist habitats. Some tortoises may need even warmer habitats, so find out what the requirements are for your species. You can increase the humidity by moistening the substrate, especially in the area under the basking lamp. You can tilt the pen slightly to keep all of the moisture on one side. This will provide your tortoise with different micro-climates to choose from.
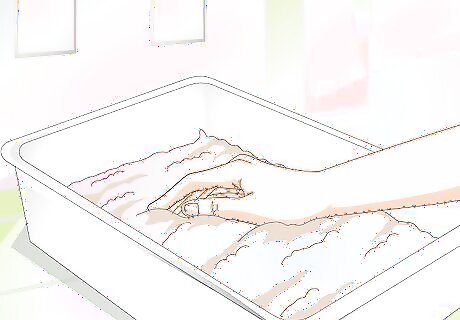
Use the proper base material. There are lots of different bedding materials available at pet stores, but not all of them are good for tortoises. A combination of soft earth and sand is the ideal base layer for tortoises. Many would add some water in the soil and then thoroughly mix it while discarding any unwanted objects in the process, this will prolong the substrate's freshness which reduces the frequency of substrate changes. Adding critters such as Earthworms, Springtails, and Pillbugs can help the substrate last much longer through aeration and eating leftover food.
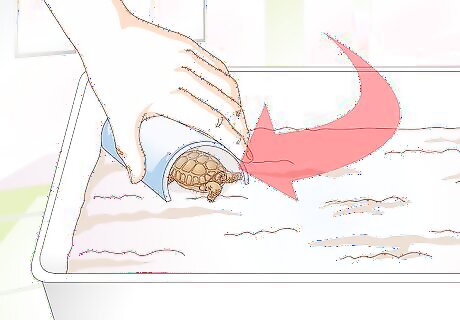
Give the tortoise places to hide. Be sure to include various different items that your tortoise can hide under if it wants. This will provide it with both shade and security.
Keeping Your Tortoise Hydrated and Nourished

Provide drinking water. Be sure to provide your tortoise with a shallow bowl of water for drinking. Change the water regularly to keep it fresh. Don't be too alarmed if your tortoise doesn't seem to drink much. Some species, especially those that are native to arid climates, drink very little water, but it's still a good idea to have it available for them.

Soak your tortoise every week. Every one to two weeks, you should soak your tortoise in a bowl of room temperature water for approximately 15-20 minutes. This will help keep the tortoise hydrated. Make sure the water doesn't go any higher than the tortoise's chin. The tortoise may start drinking while it is soaking, so make sure the water stays clean.
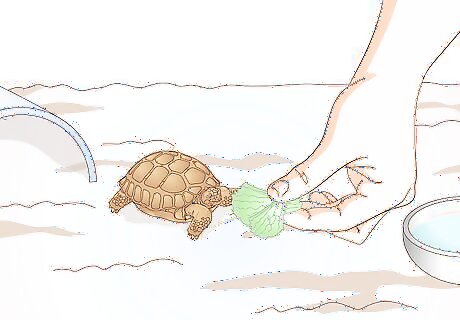
Feed your tortoise a varied diet. Tortoises all need to be fed a varied diet in order to ensure that they get all of the nutrients they need. Each species of tortoise, however, has its own specific dietary needs. Be sure to identify the species of tortoise that you have and feed it a diet that is recommended for that species. Desert tortoises should be fed a combination of grasses, leafy greens, and cactus flowers, with a small amount of fruit. Grassland grazers like leopard tortoises should be fed a variety of grasses and leafy green vegetables. You should not feed them other vegetables, or meat. A strawberry every now and then is ok. just don't feed them fruit every day.

Provide vitamins. It's extremely important to supplement a baby tortoise's diet with vitamin D3 and calcium. Tortoises can die without these nutrients, so don't skip this step! A multivitamin is also good for balancing out nutritional needs. You can buy supplements in powder form at any store that sells supplies for tortoises. You can also crush supplements that come in pill form.
Keeping Your Tortoise Safe and Healthy
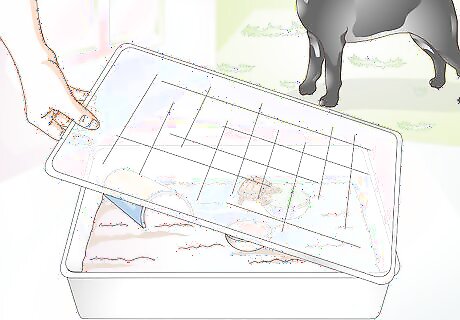
Protect your tortoise from predators. Baby tortoises are extremely vulnerable to predators because they are so small. Take extra care to protect them from animals like dogs, cats, raccoons, and birds. If you are keeping your tortoise indoors, make sure your other pets do not have access to the enclosure. If you bring your tortoise outside, be sure to cover the pen with a sturdy metal mesh top to keep predators out.

Keep handling to a minimum. Baby tortoises become stressed easily, so it's important to avoid over-handling them. Gentle petting and hand-feeding are fine, but you should wait until the tortoise is bigger to begin handling it more. If you do handle the tortoise, be careful not to distress it by flipping it over or dropping it. Do not allow children to handle the tortoise without supervision or for long periods of time.
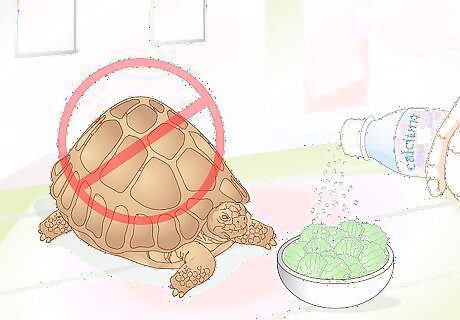
Prevent pyramiding. Pyramiding is a condition that is very common among tortoises that are raised in captivity. It occurs when the shell grows in an abnormal way, causing it to become ridged instead of smooth. This condition typically starts developing in the first year or two of life. Pyramiding may be due to calcium deficiency and/or humidity levels. Try increasing your tortoise's calcium intake by dusting his food with a balanced calcium supplement. You can also try increasing the humidity level in the pen.
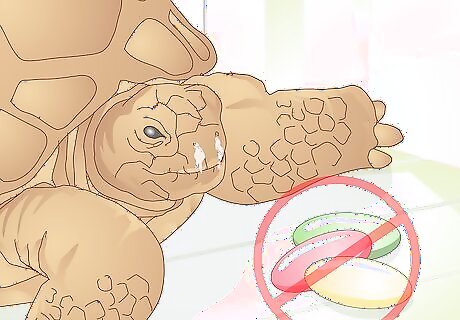
Prevent respiratory disease. Respiratory disease is fairly common in captive tortoises. The term "Runny nose syndrome" (RNS) is used to describe upper respiratory infections in tortoises. You can prevent your tortoise from developing this condition by ensuring that the habitat is well-maintained. Never feed your tortoise junk food, even if it seems to enjoy it. Always stick to the recommended diet for your species. Be careful not to keep the habitat too moist. There should always be some dry land available. Let your tortoise have as much exposure to natural sunlight as possible. Use a substrate material that will not create dust or get lodged in your tortoise's nose. It's also important to reduce the tortoise's stress and not overcrowd the habitat with too many tortoises.

















Comments
0 comment