
views
Getting Acquainted with Different Investment Vehicles

Make sure you have a safety net. Holding some money in reserve is a good idea because (a) if you lose your investment you'll have something to fall back on, and (b) it will allow you to be a bolder investor, since you won't be worried about risking every penny you own. Save between three and six months' worth of expenses. Call it your emergency fund, set aside for large, unexpected expenses (job loss, medical expenses, auto accident, etc.). This money should be in cash or some other form that's very conservative and immediately available. Once you have an emergency fund established, you can start to save for your long-term goals, like buying a home, retirement, and college tuition. If your employer offers a retirement plan, this is a great vehicle for saving, because it can save on your tax bill, and your employer may contribute money to match some of your own contributions, which amounts to "free" money for you. If you don't have a retirement plan through your workplace, most employees are allowed to accumulate tax-deferred savings in a traditional IRA or a Roth IRA. If you are self-employed, you have options like a SEP-IRA or a "SIMPLE" IRA. Once you've determined the type of account(s) to set up, you can then choose specific investments to hold within them. Get current on all your insurance policies. This includes auto, health, homeowner's/renter's, disability, and life insurance. With luck you'll never need insurance, but it's nice to have in the event of disaster.
Learn a little bit about stocks. This is what most people think of when they consider "investing." Put simply, a stock is a share in the ownership of a business, a publicly-held company. The stock itself is a claim on what the company owns — its assets and earnings. When you buy stock in a company, you are making yourself part-owner. If the company does well, the value of the stock will probably go up, and the company may pay you a "dividend," a reward for your investment. If the company does poorly, however, the stock will probably lose value. The value of stock comes from public perception of its worth. That means the stock price is driven by what people think it's worth, and the price at which a stock is purchased or sold is whatever the market will bear, even if the underlying value (as measured by certain fundamentals) might suggest otherwise. A stock price goes up when more people want to buy that stock than sell it. Stock prices go down when more people want to sell than buy. In order to sell stock, you have to find someone willing to buy at the listed price. In order to buy stock, you have to find someone selling their stock at a price you like. The job of a stockbroker is to pair up buyers and sellers. "Stocks" can mean a lot of different things. For example, penny stocks are stocks that trade at relatively low prices, sometimes just pennies. Various stocks are bundled into what's called an index, like the Dow Jones Industrials, which is a list of 30 high-performing stocks. An index is a useful indicator of the performance of the whole market.
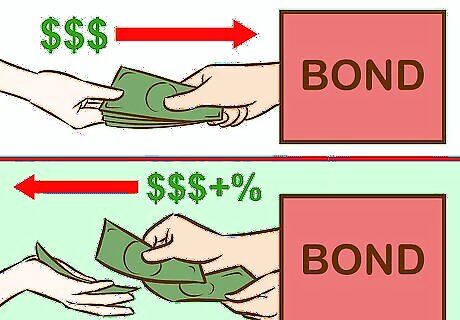
Familiarize yourself with bonds. Bonds are issuances of debt, similar to an IOU. When you buy a bond, you're essentially lending someone money. The borrower ("issuer") agrees to pay back the money (the "principal") when the life ("term") of the loan has expired. The issuer also agrees to pay interest on the principal at a stated rate. The interest is the whole point of the investment. The term of the bond can range from months to years, at the end of which period the borrower pays back the principal in full. Here's an example: You buy a five-year municipal bond for $10,000 with an interest rate of 2.35%. Thus, you lend the municipality $10,000. Each year the municipality pays you interest on your bond in the amount of of 2.35% of $10,000, or $235. After five years the municipality pays back your $10,000. So you've made back your principal plus a profit of $1175 in interest (5 x $235). Generally the longer the term of the bond, the higher the interest rate. If you're lending your money for a year, you probably won't get a high interest rate, because one year is a relatively short period of risk. If you're going to lend your money and not expect it back for ten years, however, you will be compensated for the higher risk you're taking, and the interest rate will be higher. This illustrates an axiom in investing: The higher the risk, the higher the potential return. But higher risk often means higher potential for loss for many investments.

Understand the commodities market. When you invest in something like a stock or a bond, you invest in the business represented by that security. The piece of paper you get is worthless, but what it promises is valuable. A commodity, on the other hand, is something of inherent value, something capable of satisfying a need or desire. Commodities include pork bellies (bacon), coffee beans, oil, natural gas, and potash, among many other items. The commodity itself is valuable, because people want and use it. People often trade commodities by buying and selling "futures." A future is simply an agreement to buy or sell a commodity at a certain price sometime in the future. Futures were originally used as a "hedging" technique by farmers. Here's a simple example of how it works: Farmer Joe grows avocados. The price of avocados, however, is typically volatile, meaning that it goes up and down a lot. At the beginning of the season, the wholesale price of avocados is $4 per bushel. If Farmer Joe has a bumper crop of avocados but the price of avocados drops to $2 per bushel in April at harvest, Farmer Joe may lose a lot of money. Joe, in advance of harvest as insurance against such a loss, sells a futures contract to someone. The contract stipulates that the buyer of the contract agrees to buy all of Joe's avocados at $4 per bushel in April. Now Joe has protection against a price drop. If the price of avocados goes up, he'll be fine because he can sell his avocados at the market price. If the price of avocados drops to $2, he can sell his avocados at $4 to the buyer of the contract and make more than other farmers who don't have a similar contract. The buyer of a futures contract always hopes that the price of a commodity will go up beyond the futures price he paid. That way he can lock in a lower-than-market price. The seller hopes that the price of a commodity will go down. He can buy the commodity at low (market) prices and then sell it to the buyer at a higher-than-market price.

Know a bit about investing in property. Investing in real estate can be a risky but lucrative proposition. There are lots of ways you can invest in property. You can buy a house and become a landlord. You pocket the difference between what you pay on the mortgage and what the tenant pays you in rent. You can also flip homes. That means you buy a home in need of renovations, fix it up, and sell it as quickly as possible. Real estate can be a profitable vehicle for some, but it is not without substantial risk involving property maintenance and market value. Other ways of gaining exposure to real estate include collateralized mortgage obligations (CMOs) and collateralized debt obligations (CDOs), which are mortgages that have been bundled into securitized instruments. These, however, are tools for sophisticated investors: their transparency and quality can vary greatly, as revealed during the 2008 downturn. Some people think that home values are guaranteed to go up. History has shown otherwise: real estate values in most areas show very modest rates of return after accounting for costs such as maintenance, taxes and insurance. As with many investments, real estate values do invariably rise if given enough time. If your time horizon is short, however, property ownership is not a guaranteed money-maker. Property acquisition and disposal can be a lengthy and unpredictable process and should be viewed as a long-term, higher-risk proposition. It is not the type of investment that is appropriate if your time horizon is short and is certainly not a guaranteed investment.
Learn about mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Mutual funds and ETFs are similar investment vehicles in that each is a collection of many stocks and/or bonds (hundreds or thousands in some cases). Holding an individual security is a concentrated way of investing – the potential for gain or loss is tied to a single company – whereas holding a fund is a way to spread the risk across many companies, sectors or regions. Doing so can dampen the upside potential but also serves to protect against the downside risk. Commodities exposure is usually achieved by holding futures contracts or a fund of futures contracts. Real estate can be held directly (by owning a home or investment property) or in a real estate investment trust (REIT) or REIT fund, which holds interests in a number of residential or commercial properties.
Mastering Investment Basics
Buy undervalued assets ("buy low, sell high"). If you're talking about stocks and other assets, you want to buy when the price is low and sell when the price is high. If you buy 100 shares of stock on January 1st for $5 per share, and you sell those same shares on December 31st for $7.25, you just made $225. That may seem a paltry sum, but when you're talking about buying and selling hundreds or even thousands of shares, it can really add up. How do you tell if a stock is undervalued? You need to look at a company closely — its earnings growth, profit margins, its P/E ratio, and its dividend yield — instead of looking at just one aspect and making a decision based on a single ratio or a momentary drop in the stock's price. The price-to-earnings ratio is a common way of determining if a stock is undervalued. It simply divides a company's share price by its earnings. For example, if Company X is trading at $5 per share, with earnings of $1 per share, its price-to-earnings ratio is 5. That is to say, the company is trading at five times its earnings. The lower this figure, the more undervalued the company may be. Typical P/E ratios range between 15 and 20, although ratios outside that range are not uncommon. Use P/E ratios as only one of many indications of a stock's worth. Always compare a company to its peers. For example, assume you want to buy Company X. You can look at Company X's projected earnings growth, profit margins, and price-to-earnings ratio. You would then compare these figures to those of Company X's closest competitors. If Company X has better profit margins, better projected earnings, and a lower price-to-earnings ratio, it may be a better buy. Ask yourself some basic questions: What will the market be for this stock in the future? Will it look bleaker or better? What competitors does this company have, and what are their prospects? How will this company be able to earn money in the future? These should help you come to a better understanding of whether a company's stock is under- or over-valued.

Invest in companies that you understand. Perhaps you have some basic knowledge regarding some business or industry. Why not put that to use? Invest in companies or industries that you know, because you're more likely to understand revenue models and prospects for future success. Of course, never put all your eggs in one basket: investing in only one -- or a very few -- companies can be quite risky. However, wringing value out of a single industry (whose workings you understand) will increase your chances of being successful. For example, you may hear plenty of positive news on a new technology stock. It is important to stay away until you understand the industry and how it works. The principle of investing in companies you understand was popularized by renowned investor Warren Buffett, who made billions of dollars sticking only with business models he understood and avoiding ones he did not.

Avoid buying on hope and selling on fear. It's very easy and too tempting to follow the crowd when investing. We often get caught up in what other people are doing and take it for granted that they know what they're talking about. Then we buy stocks just because other people buy them or sell them when other people do. Doing this is easy. Unfortunately, it's a good way to lose money. Invest in companies that you know and believe in — and tune out the hype — and you'll be fine. When you buy a stock that everyone else has bought, you're buying something that's probably worth less than its price (which has probably risen in response to the recent demand). When the market corrects itself (drops), you could end up buying high and then selling low, just the opposite of what you want to do. Hoping that a stock will go up just because everyone else thinks it will is foolish. When you sell a stock that everyone else is selling, you're selling something that may be worth more than its price (which likely has dropped because of all the selling). When the market corrects itself (rises), you've sold low and will have to buy high if you decide you want the stock back. Fear of losses can prove to be a poor reason to dump a stock. If you sell based on fear, you may protect yourself from further declines, but you may also miss out on a rebound. Just as you did not anticipate the decline, you will not be able to predict the rebound. Stocks have historically risen over long time frames, which is why holding on to them and not over-reacting to short-term swings is important.
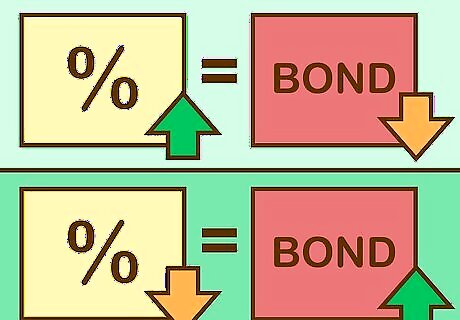
Know the effect of interest rates on bonds. Bond prices and interest rates have an inverse relationship. When interest rates go up, bond prices go down. When interest rates go down, bond prices go up. Here's why: Interest rates on bonds normally reflect the prevailing market interest rate. Say you buy a bond with an interest rate of 3%. If interest rates on other investments then go up to 4% and you're stuck with a bond paying 3%, not many people would be willing to buy your bond from you when they can buy another bond that pays them 4% interest. For this reason, you would have to lower the price of your bond in order to sell it. The opposite situation applies when bond market rates are falling.

Diversify. Diversifying your portfolio is one of the most important things that you can do, because it diminishes your risk. Think of it this way: If you were to invest $5 in each of 20 different companies, all of the companies would have to go out of business before you would lose all your money. If you invested the same $100 in just one company, only that company would have to fail for all your money to disappear. Thus, diversified investments "hedge" against each other and keep you from losing lots of money because of the poor performance of a few companies. Diversify your portfolio not only with a good mix of stocks and bonds, but go further by buying shares in companies of different sizes in different industries and in different countries. Often when one class of investment performs poorly, another class performs nicely. It is very rare to see all asset classes declining at the same time. Many believe a balanced or "moderate" portfolio is one made up of 60% stocks and 40% bonds. Thus, a more aggressive portfolio might have 80% stocks and 20% bonds, and a more conservative portfolio might have 70% bonds and 30% stocks. Some advisors will tell you that your portfolio's percentage of bonds should roughly match your age.
Invest for the long run. Choosing good-quality investments can take time and effort. Not everyone can do the research and keep up with the dynamics of all the companies being considered. Many people instead employ a "buy and hold" approach of weathering the storms rather than attempting to predict and avoid market downturns. This approach works for most in the long term but requires patience and discipline. There are some, however, who choose to try their hand at being a day-trader, which involves holding stocks for a very short time (hours, even minutes). Doing so, however, does not often lead to success over the long term for the following reasons: Brokerage fees add up. Every time you buy or sell a stock, a middleman known as a broker takes a cut for connecting you with another trader. These fees can really add up if you're making a lot of trades every day, cutting into your profit and magnifying your losses. Many try to predict what the market will do and some will get lucky on occasion by making some good calls (and will claim it wasn't luck), but research shows that this tactic does not typically succeed over the long term. Historically the stock market has risen over the long term. From 1871 to 2014, the S&P 500's compound annual growth rate was 9.77%, a rate of return many investors would find attractive. The challenge is to stay invested long-term while weathering the ups and downs in order to achieve this average: the standard deviation for this period was 19.60%, which means some years saw returns as high as 29.37% while other years experienced losses as large as 9.83%. Set your sights on the long term, not the short. If you're worried about all the dips along the way, find a graphical representation of the stock market over the years and hang it somewhere you can see whenever the market is undergoing its inevitable–and temporary–declines.

Consider whether or not to short sell. This can be a "hedging" strategy, but it can also amplify your risk, so it's really suitable only for experienced investors. The basic concept is as follows: Instead of betting that the price of a security is going to increase, "shorting" is a bet that the price will drop. When you short a stock (or bond or currency), your broker actually lends you shares without your having to pay for them. Then you hope the stock's price goes down. If it does, you "cover," meaning you buy the actual shares at the current (lower) price and give them to the broker. The difference between the amount credited to you in the beginning and the amount you pay at the end is your profit. Short selling can be dangerous, however, because it's not easy to predict a drop in price. If you use shorting for the purpose of speculation, be prepared to get burned sometimes. If the stock's price were to go up instead of down, you would be forced to buy the stock at a higher price than what was credited to you initially. If, on the other hand, you use shorting as a way to hedge your losses, it can actually be a good form of insurance. This is an advanced investment strategy, and you should generally avoid it unless you are an experienced investor with extensive knowledge of markets. Remember that while a stock can only drop to zero, it can rise indefinitely, meaning that you could lose enormous sums of money through short-selling.
Starting Out
Choose where to open your account. There are different options available: you can go to a brokerage firm (sometimes also called a wirehouse or custodian) such as Fidelity, Charles Schwab or TD Ameritrade. You can open an account on the website of one of these institutions, or visit a local branch and choose to direct the investments on your own or pay to work with a staff advisor. You can also go directly to a fund company such as Vanguard, Fidelity, or T. Rowe Price and let them be your broker. They will offer you their own funds, of course, but many fund companies (such as the three just named) offer platforms on which you can buy the funds of other companies, too. See below for additional options in finding an advisor. Always be mindful of fees and minimum-investment rules before opening an account. Brokers all charge fees per trade (ranging from $4.95 to $10 generally), and many require a minimum initial investment (ranging from $500 to much higher). Online brokers with no minimum initial-investment requirement include Capital One Investing, TD Ameritrade, First Trade, TradeKing, and OptionsHouse. If you want more help with your investing, there is a variety of ways to find financial advice: if you want someone who helps you in a non-sales environment, you can find an advisor in your area at one of the following sites: letsmakeaplan.org, www.napfa.org, and garrettplanningnetwork.com. You can also go to your local bank or financial institution. Many of these charge higher fees, however, and may require a large opening investment. Some advisors (like Certified Financial Planners™) have the ability to give advice in a number of areas such as investments, taxes and retirement planning, while others can only act on a client's instructions but not give advice. It's also important to know that not all people who work at financial institutions are bound to the "fiduciary" duty of putting a client's interests first. Before starting to work with someone, ask about their training and expertise to make sure they are the right fit for you. You can also use FINRA's BrokerCheck to verify whether a person or firm is registered, as required by law, to sell securities (stocks, bonds, mutual funds and more), offer investment advice or both.

Invest in a Roth IRA as soon in your working career as possible. If you're earning taxable income and you're at least 18, you can establish a Roth IRA. This is a retirement account to which you can contribute up to an IRS-determined maximum each year (the latest limit is the lesser of $6,000 or the amount earned plus an additional $1,000 "catch up" contribution for those age 50 or older). This money gets invested and begins to grow. A Roth IRA can be a very effective way to save for retirement. You don't get a tax deduction on the amount you contribute to a Roth, as you would if you contributed to a traditional IRA. However, any growth on top of the contribution is tax-free and can be withdrawn without penalty after you turn age 59½ (or earlier if you meet one of the exceptions to the age 59½ rule). Investing as soon as possible in a Roth IRA is important. The earlier you begin investing, the more time your investment has to grow. If you invest just $20,000 in a Roth IRA before you're 30 years old and then stop adding any more money to it, by the time you're 72 you'll have a $1,280,000 investment (assuming a 10% rate of return). This example is merely illustrative. Don't stop investing at 30. Keep adding to your account. You will have a very comfortable retirement if you do. How can a Roth IRA grow like this? By compound interest. The return on your investment, as well as reinvested interest, dividends and capital gains, are added to your original investment such that any given rate of return will produce a larger profit through accelerated growth. If you are earning an average compound annual rate of return of 7.2%, your money will double in ten years. (This is known as "the rule of 72.") You can open a Roth IRA through most online brokers as well as through most banks. If you are using a self-directed online broker, you will simply select a Roth IRA as the type of account while you are registering.

Invest in your company's 401(k). A 401(k) is a retirement-savings vehicle into which an employee can direct portions of his or her paychecks and receive a tax deduction in the year of the contributions. Many employers will match a portion of these contributions, so the employee should contribute at least enough to trigger the employer match. A 403(b) is a similar option for employees of tax-exempt organizations, teachers, and others. Many employers will match a portion of these contributions, so the employee should contribute at least enough to trigger the employer match — it immediately doubles your money.
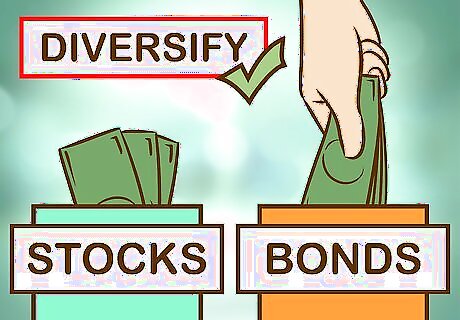
Consider investing mainly in stocks (or mutual funds that hold stocks) but also in bonds (or bond funds) to diversify your portfolio. From 1925 to 2011, stocks outperformed bonds in every rolling 25-year period. While this may sound appealing from a return standpoint, it entails volatility, which can be worrisome. Add less-volatile bonds to your portfolio for the sake of stability and diversification. The older you get, the more appropriate it becomes to own bonds (a more conservative investment). Re-read the above discussion of diversification.

Start off investing a little money in mutual funds. An index fund is a mutual fund that invests in a specific list of companies of a particular size or economic sector. Such a fund performs similarly to its index, such as the S&P 500 index or the Barclays Aggregate Bond index. Mutual funds come in different shapes and sizes. Some are actively managed, meaning there is a team of analysts and other experts employed by the fund company to research and understand a particular geographical region or economic sector. Because of this professional management, such funds generally cost more than index funds, which simply mimic an index and don't need much management. They can be bond-heavy, stock-heavy, or invest in stocks and bonds equally. They can buy and sell their securities actively, or they can be more passively managed (as in the case of index funds). Mutual funds come with fees. There may be charges (or "loads") when you buy or sell shares of the fund. The fund's "expense ratio" is expressed as a percentage of total assets and pays for overhead and management expenses. Some funds charge a lower-percentage fee for larger investments. Expense ratios generally range from as low as 0.15% (or 15 basis points, abbreviated "BPS") for index funds to as high as 2% (200 BPS) for actively managed funds. There may also be a "12b-1" fee charged to offset a fund's marketing expenses. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission states that no evidence exists that higher-fee mutual funds produce better returns than do lower-fee funds. In other words, deal with lower-fee funds. Mutual funds can be purchased through nearly any brokerage service. Even better is to purchase directly from a mutual fund company. This avoids brokerage fees. Call or write the fund company or visit their website. Opening a fund account is simple and easy. See Invest in Mutual Funds.
Consider exchange-traded funds in addition to or instead of mutual funds. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are very similar to mutual funds in that they pool people's money and buy many investments. There are a few key differences: ETFs can be traded on an exchange throughout the business day just like stocks, whereas mutual funds are bought and sold only at the end of each trading day. ETFs are typically index funds and do not generate as much in the way of taxable capital gains to pass on to investors as compared with actively managed funds. ETFs and mutual funds are becoming less distinct from each other, and investors need not own both types of investment. If you like the idea of buying and selling fund shares during (rather than at the end of) the trading day, ETFs are a good choice for you.
Making the Most of Your Money

Consider using the services of a financial planner or advisor. Many planners and advisors require that their clients have an investment portfolio of at least a minimum value, sometimes $100,000 or more. This means it could be hard to find an advisor willing to work with you if your portfolio isn't well established. In that case, look for an advisor interested in helping smaller investors. How do financial planners help? Planners are professionals whose job is to invest your money for you, ensure that your money is safe, and guide you in your financial decisions. They draw from a wealth of experience at allocating resources. Most importantly, they have a financial stake in your success: the more money you make under their tutelage, the more money they make.

Buck the herd instinct. The herd instinct, alluded to earlier, is the idea that just because a lot of other people are doing something, you should, too. Many successful investors have made moves that the majority thought were unwise at the time. That doesn't mean, however, that you should never seek investment advice from other people. Just be wise about choosing the people you listen to. Friends or family members with a successful background in investing can offer worthwhile advice, as can professional advisors who charge a flat fee (rather than a commission) for their help. Invest in smart opportunities when other people are scared. In 2008 as the housing crisis hit, the stock market shed thousands of points in a matter of months. A smart investor who bought stocks as the market bottomed out enjoyed a strong return when stocks rebounded. This reminds us to buy low and sell high. It takes courage to buy investments when they are becoming cheaper (in a falling market) and sell those investments when they are looking better and better (a rising market). It seems counter-intuitive, but it's how the world's most successful investors made their money.

Know the players in the game. Which institutional investors think that your stock is going to drop in price and have therefore shorted it? What mutual fund managers have your stock in their fund, and what is their track record? While it helps to be independent as an investor, it's also helpful to know what respected professionals are doing. There are websites that compile recent opinions on a stock from analysts and expert investors. For example, if you are considering a purchase of Tesla shares, you can search Tesla on Stockchase. It will give you all the recent expert opinions on the stock.

Re-examine your investment goals and strategies every so often. Your life and conditions in the market change all the time, so your investment strategy should change with them. Never be so committed to a stock or bond that you can't see it for what it's worth. While money and prestige may be important, never lose track of the truly important, non-material things in life: your family, friends, health, and happiness.Start Investing Step 23.jpg For example, if you are very young and saving for retirement, it may be appropriate to have most of your portfolio invested in stocks or stock funds. This is because you would have a longer time horizon in which to recover from any big market crashes or declines, and you would be able to benefit from the long-term trend of markets moving higher. If you are just about to retire, however, having much less of your portfolio in stocks, and a large portion in bonds and/or cash equivalents is wise. This is because you will need the money in the short-term, and as a result you do not want to risk losing the money in a stock market crash right before you need it.



















Comments
0 comment