views
X
Trustworthy Source
Cleveland Clinic
Educational website from one of the world's leading hospitals
Go to source
If you have hypothyroidism, you may want to lower your TSH levels so you can lessen the symptoms of your condition. You can take thyroid medication to treat high TSH levels. You can also make dietary and lifestyle changes to address your hypothyroidism.
Adjusting Your Diet and Lifestyle
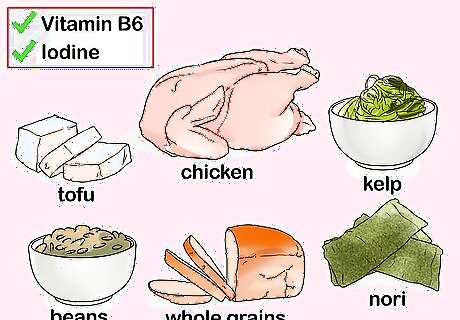
Maintain a diet rich in Vitamin B and iodine. Have a diet rich in healthy sources of protein like tofu, chicken, and beans as well as Vitamin B rich foods like whole grains, nuts, and seeds. Add a good balance of fruits and vegetables to your diet, specifically sea vegetables, as they are rich in iodine. Foods high in natural iodine are good for your thyroid. You could try having sea vegetables like kelp, nori, and kombu at least once a day. Sprinkle kelp over your salads or soups for added iodine. Add kombu to your beans or meat. Wrap foods in nori. Add nuts and seeds to stir fries, quinoa, and salads.

Exercise regularly. Exercise can help boost your metabolism and counteract some of the side effects of an underactive thyroid, such as fatigue, depression and weight gain. Go for regular runs or bike rides. Join a gym and take workout classes. Make it a habit to be active for at least 30 minutes a day. You can also try taking a yoga class to help you stay active and to reduce your stress levels. Look for yoga classes at your local gym or yoga studio.

Get enough Vitamin D every day. Aim to get at least 20 to 30 minutes of sun exposure in the early morning or the evening. Expose your arms, legs, and face to the sun. Low vitamin D levels have been found to be associated with hypothyroidism. Bringing those levels up may improve your symptoms of hypothyroidism. If you live in an area that gets very little direct sunlight, especially during the winter months, speak to your doctor about taking Vitamin D supplements.

Reduce stress and anxiety. Keep your stress and anxiety levels low to avoid agitating your thyroid. Do relaxing activities like painting, drawing, and knitting. Try doing a hobby you enjoy to release stress and anxiety. Working out can also be a good way to reduce your stress levels. You can also do deep breathing exercises to help reduce your stress levels or take a weekly yoga class.
Taking Thyroid Medication
Have your TSH levels tested. If you are exhibiting some of the effects of hypothyroidism, such as constipation, hoarseness, and fatigue, go to the doctor to discover for sure whether or not you have hypothyroidism. At the appointment, your doctor will do a blood test to find out if your thyroid is underactive.

Ask your doctor for a prescription for thyroid medication. The most reliable way to lower your TSH levels due to hypothyroidism is to take a synthetic thyroid hormone called levothyroxine. This drug is available by prescription from your doctor. It is an oral medication that restores your hormone levels and reverses the symptoms of hypothyroidism. You will need to take it once a day. Once you begin taking medication, your symptoms should start to improve within 3-5 days. The medication should be fully effective in 4-6 weeks. Always follow your doctor's instructions on dosage. Never take more than the recommended dose of the medication. Thyroid medication must be taken for life to maintain lower TSH levels, but luckily, it is relatively inexpensive. Your doctor will break down the exact costs for the medication.

Learn the side effects of the medication. If you have a dose that is too high and you get an excessive amount of the thyroid hormone, you can experience side effects. Your doctor may need to adjust your dosage to fit your body's needs. You may also be prescribed a specific medication that your body doesn't respond well to. Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to levothyroxine: hives; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms: Fast or irregular heart rate Chest pain and/or difficulty breathing Fever, hot flashes, and/or excessive sweating Feeling unusually cold Weakness, tiredness, and/or sleep problems Memory problems, feeling depressed, or feeling irritable Muscle aches Dryness of skin, dryness of hair, or hair loss Changes in your menstrual periods Vomiting, diarrhea, appetite changes, and or weight changes
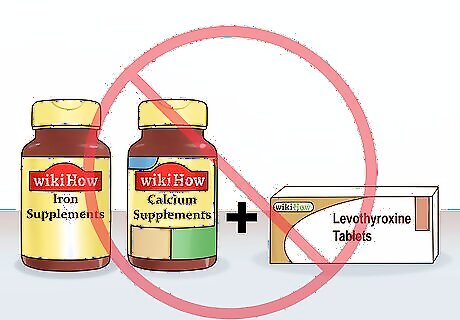
Do not take certain supplements while on the medication. Iron and calcium supplements can affect your body's ability to absorb the medication. You should also avoid having medications that contain cholestyramine and aluminum hydroxide. Speak to your doctor if you are on other medications or supplements before you take thyroid medication. Generally, thyroid medication is most effective when taken on an empty stomach about 30 minutes before eating.
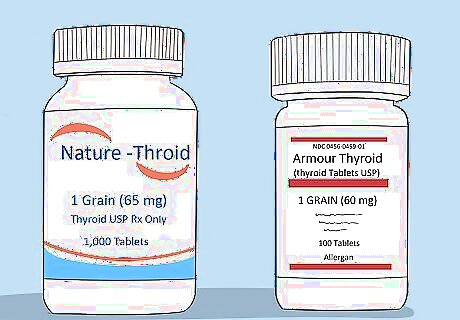
Try “natural” thyroid medications with caution. “Natural” thyroid replacement medication comes from animal thyroids, usually pigs. You can buy it online as a food supplement. However, the medication is not purified and not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Avoid buying or taking any “natural” thyroid medication that is not prescribed or recommended by your doctor. You can be prescribed these “natural” alternative medication options in either extract or desiccated form. If you're interested in learning more, ask your doctor about Armour Thyroid, a natural thyroid extract that is available by prescription.
Monitor your progress on the medication. Have regular check ins with your doctor to confirm your TSH levels are going down with the help of the medication. In some cases, your doctor may adjust your dosage after two to three months to ensure your body is getting enough of the hormone. After one to two months on the medication at the correct dose, your symptoms should improve and you should feel less tired. Your eating habits and weight should also improve.
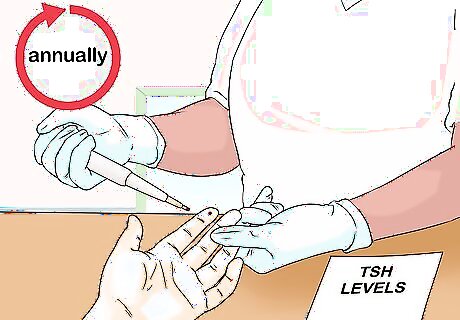
Get your TSH levels tested every 6-12 months. Arrange for an annual test with your doctor to ensure your TSH levels are where they should be. Your doctor should test your levels at least once a year to confirm the medication is working. You may need to get your levels tested more frequently if you're on a new dose of levothyroxine. Taking thyroid hormone replacement medication is a lifelong requirement for people with hypothyroidism. Do not stop taking your medication if you start to feel better, as your symptoms will likely return.



















Comments
0 comment