views
Preparing the Planting Area
Choose somewhere that gets at least 6 hours of sun per day. Most types of running bamboo are the hardiest varieties of bamboo that exist, and they need lots of sun to grow well. The area where you’re planting your bamboo should get at least 6 hours and up to 10 hours of sun a day.
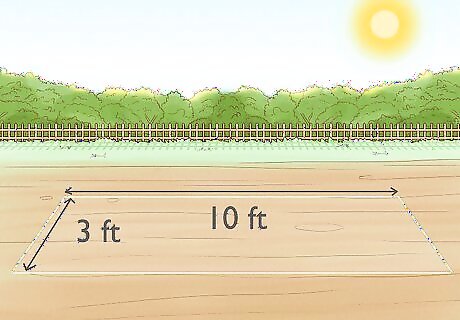
Measure out your planting plot. The area where you plant your bamboo should measure at least 3 ft (1 meter) by 10 ft (3 meters) to accommodate the rhizomes of the plant and allow for their growth. Running bamboo will grow to fill whatever space it has, so you can also make your planting area larger. Your planting area doesn’t have to be in the shape of a rectangle. An oval or circle also works well for bamboo. An oval should be at least 3 ft (1 meter) wide at its widest point and at least 10 ft (3 meters) long. A circle should be at least 10 ft in diameter. If you’re planting in a container, choose it based on how wide you want the bamboo to grow. The planter should be at least 3 feet (1 meter) wide and 5 feet (1.5 meters) long. You can set several containers next to one another to extend the length of the planting area.
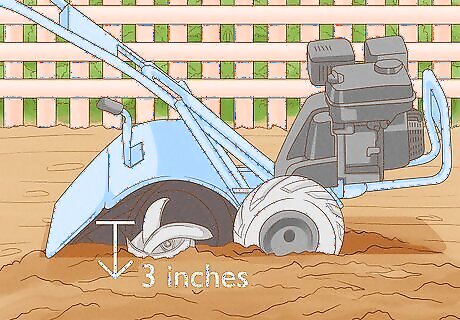
Till the soil. Bamboo prefers loose soil, so the more you till your soil, the better. You should till down to a depth of 3 inches (7.5 cm). Make sure you break up any clumps in the soil. You can also till in a standard potting soil if your soil is a bit dry. You should use about half as much potting soil as the amount of soil it's being tilled into. Bamboo is pretty hardy, so you can use your favorite potting soil for this step.
Creating a Barrier for Running Bamboo
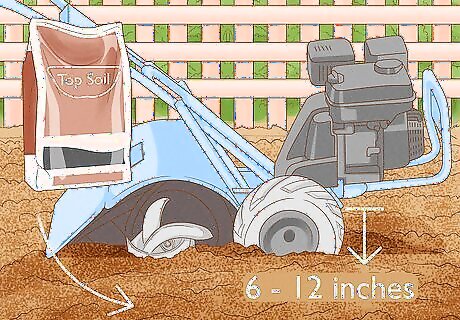
Use topsoil to create a raised bed. You should mix a good topsoil with the existing soil down to a depth of about 12 inches (30 cm). Make sure that the raised bed of soil is raised 6 to 12 inches above the existing soil around the planting area. The natural border this creates, where the raised bed tapers off, prevents the running bamboo from spreading.
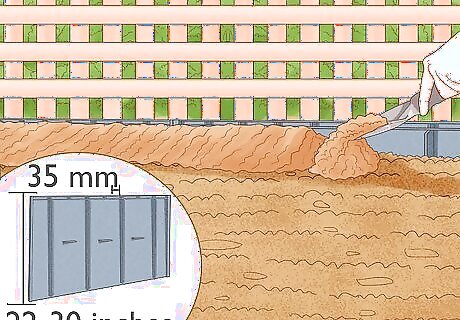
Install a bamboo barrier. If you prefer not to create a raised bed, you can plant a bamboo barrier. You should use a barrier that is 22 to 30 inches (56 to 76 cm) tall and about 35 mm (1.4 inches) thick. After you’ve buried the barrier around the perimeter of your planting area, compact the soil next to the barrier. The density of that soil will make it harder for the rhizomes to grow through.
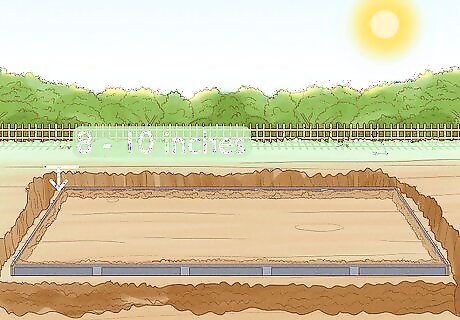
Dig a trench. The trench should be 8 to 10 inches deep and a few inches wide and should extend all the way around the planting area. This creates a natural barrier and will allow you to see if rhizomes grow out of that area. If they do, trim them with shears.
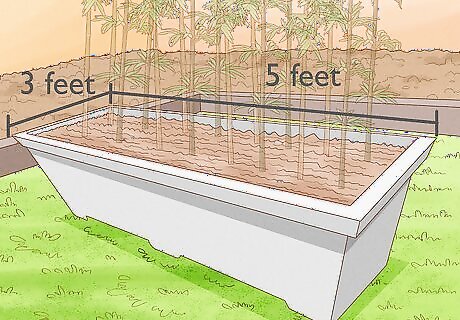
Plant your bamboo in a planter. An easy way to contain running bamboo is to plant it in a planter. The planter should be at least 3 feet (1 meter) wide and 5 feet (1.5 meters) long, but it can be wider and longer if you’d like a thicker wall of bamboo. Bamboo planted in a planter will likely not reach its full height. If you plant in a planter, you’ll also need to divide or transplant the bamboo every 3 to 5 years to ensure it continues to stay healthy. If you decide to plant in a planter, you can follow the same directions as planting in soil – just make sure you place each plant in the center of the planter.
Positioning the Bamboo
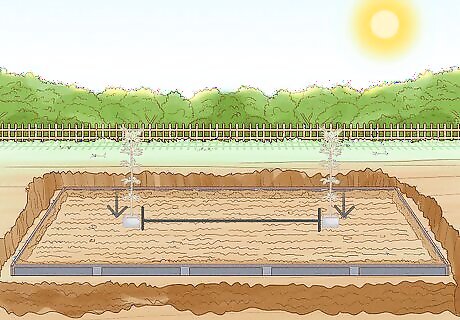
Space the bamboo plants 3 to 5 feet (1 to 1.5 meters) apart. Anything less than 3 feet will reduce the eventual height of the bamboo plant. Bamboo plants planted 6 to 8 feet (2 to 2.5 m) apart will take a few years longer to fully grow in.
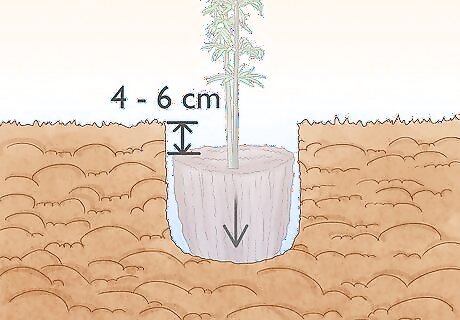
Dig a hole no deeper than the container the bamboo came in. Running bamboo does the best when it’s planted no more than a few inches (4 to 6 cm) from the top of the soil. Dig a hole just slightly wider than the plant and a few inches deep.

Till in organic material at the bottom of the hole. You can use topsoil, wood chips, or compost, because bamboo will grow well in most types of organic material. Tilling those materials into the bottom of the hole ensures that the plant can drain and root well. You should use only enough organic material to cover about 1 inch (2.5 cm) of the hole.
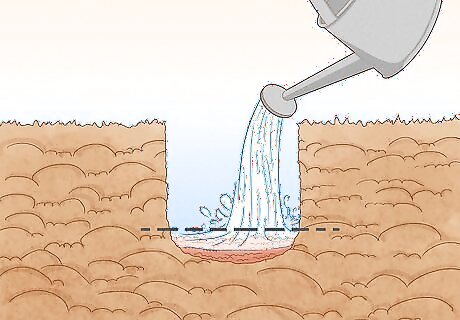
Wet the hole for planting. Bamboo requires a bit of water to grow well, so wetting the hole first ensures it grows more quickly. Don’t put so much water in the hole that it starts to create a puddle, but the soil should be pretty soaked.
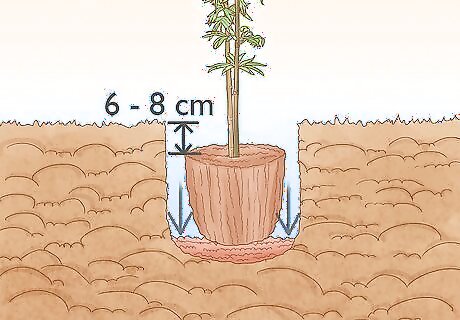
Place the bamboo in the hole. The rhizome should be placed horizontally in the center of the hole, a few inches (6 to 8 cm) below the hole's surface. Then loosely cover the rhizome with topsoil until the hole is full. Make sure you get soil on top of and next to the rhizome to cover it completely. Bamboo grows best in loose soil, so don’t pack the soil in as you would with other plants.

Cover the soil with mulch. You should spread the mulch to a depth of 2 or more inches (5 or more centimeters) since this will encourage decomposition under the mulch. The nutrients released by the decomposition process will help the bamboo grow quickly. The type of much you use doesn't matter, as long as you are using an organic mulch.
Taking Care of the Bamboo After It’s Planted
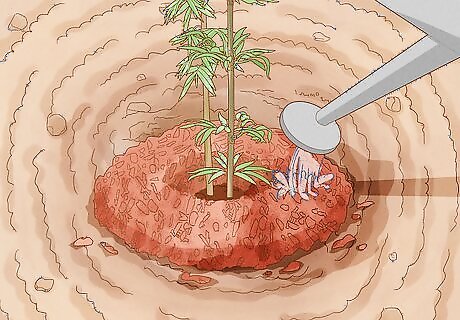
Water your bamboo frequently. While bamboo is still growing, it needs a lot of water. If the weather is mild, water your bamboo twice a week or so. If it’s very hot or windy, you might want to water every day. Soak the soil around your bamboo each time you water it. If the soil looks brown or dry, your bamboo isn't getting enough water.
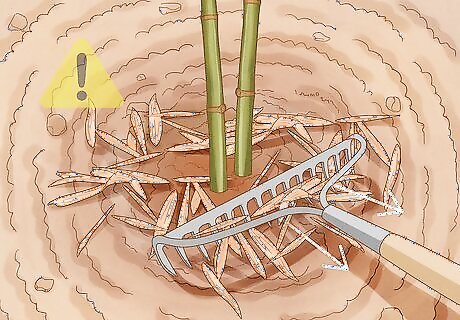
Leave falling leaves alone. Bamboo plants will lose their leaves during the fall, when they’ll yellow and fall to the ground. Don’t rake these leaves. They’ll eventually decompose into the soil, creating a source of nutrients for the bamboo.
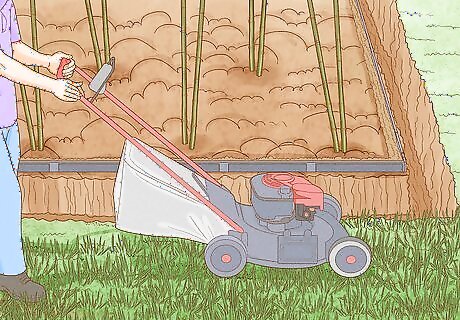
Prune or mow the edges of the bamboo. If you’ve planted your bamboo near your lawn, make sure you mow the edges near the bamboo planting area frequently. Frequent moving prevents the rhizomes from getting into your grass. If you have a trench dug around your bamboo, check it regularly during the spring to make sure no rhizomes are growing out. If they are, you can trim them with pruning shears.

Divide and transplant your bamboo. If your bamboo is running out of space, you can divide and transplant the current plant. You should only do this to plants that are older than 1 year old. Choose how much of the bamboo you want to remove, and then dig down into the soil until you reach the rhizome for that section. Drive a sharp shovel into the rhizome to make a break in the rhizome. You might need to pour some water onto the rhizome to make it easier to break up. Pull the separated section of bamboo apart with your hands and remove it from the hole. Fill the soil back in by the existing bamboo, making sure to water the area. Then replant the section of bamboo you removed in a new area, following the directions above.

Watch for common problems. Like all plants, there are certain diseases and other problems that can affect bamboo, so it is important to watch out for these. If you need to prune your bamboo, make sure to sterilize your tools after using rubbing alcohol to prevent the spread of diseases. Some common problems to watch for include: Fungal spots. This problem usually affects older plants, and the best solution is to cut away the old growth to make way for the new growth. Sooty mold. This is due to the secretions of sucking pests, such as aphids. If you notice this problem, then you will need to do several applications of insecticide soap until the problem resolves. Root rot. This can kill the entire plant if it is not taken care of. If you notice that the roots are rotting, then you will need to cut away the plant from the roots and repot it. Bamboo mosaic virus. This disease will likely kill your plant no matter what you do, but you can prolong the life of your bamboo plant by pruning it frequently.












Comments
0 comment