views
Executing a Chest Roll
Make sure you're stretched and limber. Before doing any gymnastic maneuver, it's imperative that you properly stretch and train your body. Because of the nature of a chest roll, you'll want to pay special attention to your back, neck, and abdomen. Attempting a maneuver without proper stretching can cause serious injuries, including dislocations, muscle strains, and spinal injuries. Practice and perfect the form of a gymnastic move (in this case, the chest roll) before attempting to actually do it as a moving maneuver. Be sure that your back and neck are loose and well-stretched. Attempting a chest roll without stretching or working on your form could cause serious injuries, and will set your training back significantly.
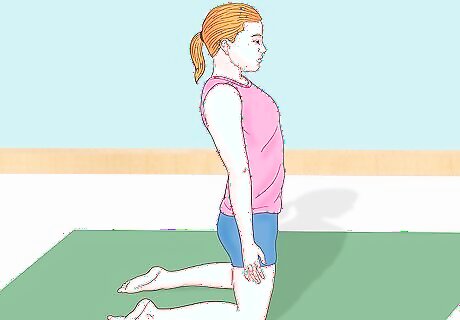
Get into position. The starting position for a chest roll is to kneel while facing the direction you'll be rolling. It's a good idea to have a gymnastics mat on the floor, so make sure you're at an end of the mat and will have sufficient room to roll forward. Kneel with your feet out behind you. Don't sit back on your feet - make sure that you are kneeling with your body in an upright position. Extend your hands out at your sides with your palms open and facing forward.
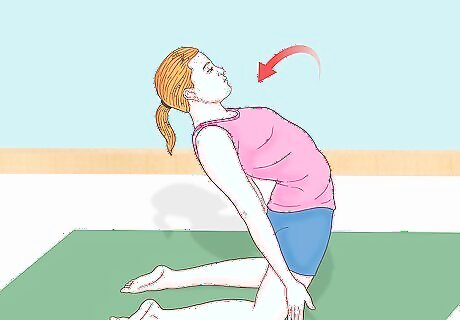
Begin bending. From the kneeling position, you'll want to begin bending your body in preparation before you actually roll off your knees. To do this, you'll need to push your hips forward while arching your back. Keep your hands slightly forward and angled down, and make sure your palms remain open and forward. Your back should be arched back above or past your hips.
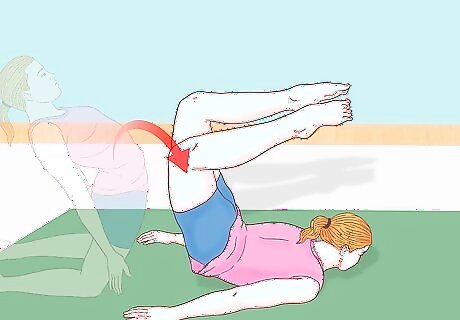
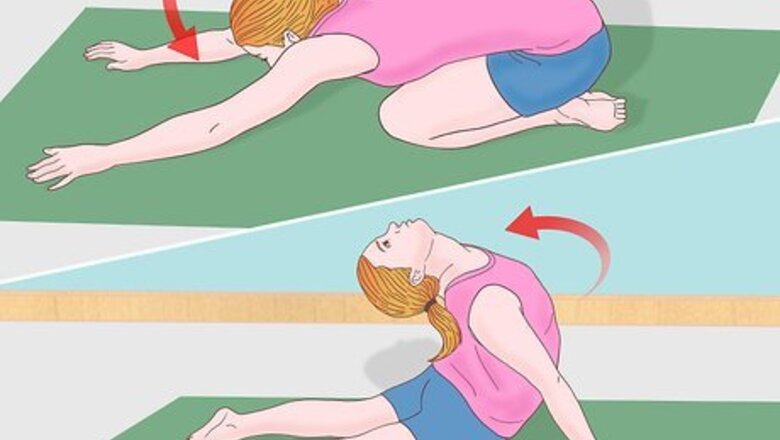
Roll forward. With your back arched, you'll roll forward, letting the palms of your hands soften the downward momentum and guide your body into the roll. Roll onto your stomach first, then let your body continue forward until you're on your chest. Rest the side of your face on the mat in front of you. Once you've rolled onto your chest you'll maintain that position, which is known as a chest stand. Keep your back arched, even in the chest stand. You may poise your legs above your head, keeping your feet close together, or if you're more advanced you may push even further and let your feet touch the floor while in a chest stand. Do not attempt to touch your feet to the floor unless you've had sufficient training and supervision, ideally with a trained gymnast. Keep your palms flat on the floor (or mat) once you've rolled onto your chest. Your hands will help stabilize your body as you maintain the chest stand. If you need to move your arms slightly outward for better stability, you may do so once you're in the chest stand.
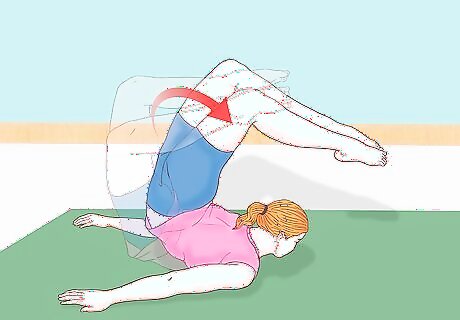
Exit the chest roll. From the chest stand, you can either continue into a subsequent gymnastic position, lie flat and exit the roll, or stand and finish the maneuver. If you're just starting out, you should simply return your body to a downward-facing position flat on the mat and exit the maneuver.
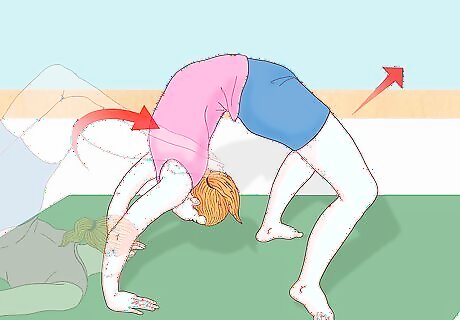
Stand and finish the chest roll (optional). If you're new to gymnastics, it's best to work on perfecting the chest roll and chest stand before attempting to incorporate other moves. Once you're more advanced, though, you can enter a bridge (sometimes called a "wheel" in yoga) and push forward into a standing position. Put your feet flat on the ground, like you would during a fully-rolled chest stand. Push up with your hands, keeping your palms flat against the floor/matt. Rotate your wrists so that your fingers face ahead of you instead of behind you. Enter a "bridge" position, where your hands and feet are the only parts of your body touching the floor. Keep your back arched, but make sure your arms and legs are straight (but not locked) and close together. Push forward, continuing your momentum towards a full standing position. Remember that this takes a long time to perfect, and should not be rushed. Attempting to complete the roll into a bridge position without proper training could result in serious injury.
Stretching and Training to Do a Chest Roll
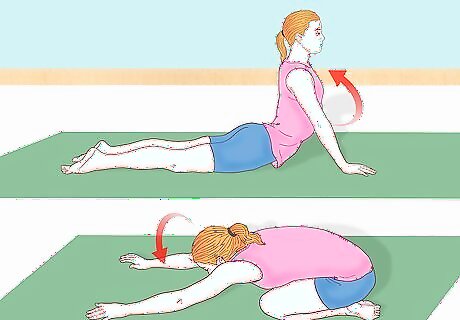
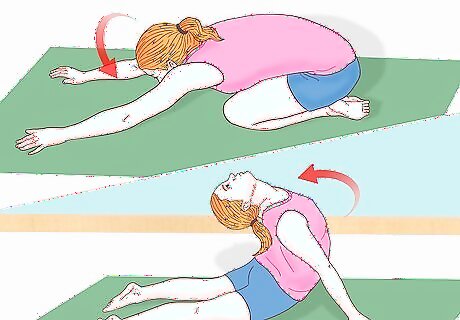
Use yoga to stretch your back. Before attempting to execute a chest roll, it's imperative that you stretch your back. The best way to prepare for this move is by engaging in the yoga positions "Cobra Pose" (Bhujangasana) and "Child's Pose" (Bālāsana). To do the Cobra Pose, lie flat on your stomach with your palms flat on the floor under your shoulders. Inhale while lifting your head and chest off the floor, keeping your neck aligned with your spine. Try to push your shoulders down and back while pushing your chest forward. To do the Child's Pose, kneel on the floor with your feet touching under your hips. Bend forward and stretch your arms out ahead of you while touching your forehead to the floor.
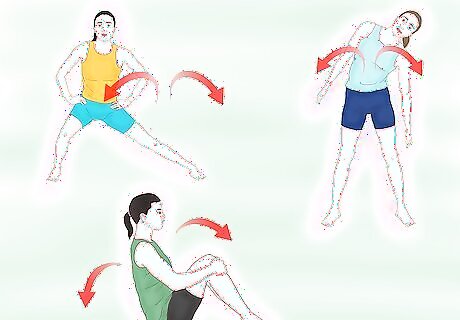
Practice dynamic stretching. Dynamic stretching involves the use of movement and momentum to stretch the body. These types of stretches have been shown to be more effective at preparing the body for athletic/gymnastic competition. Do side bends - stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Lean to one side while keeping your torso straight, then lean to the other side, all without bending forwards/backwards. Try trunk rotations - while standing with feet shoulder-width apart and hands on hips, turn from side to side. Keep your feet planted on the floor and bend your knees slightly as you swing from side to side. Do a full back stretch - this will build off of the other back stretches. While lying on your back, tuck your knees to your chest and wrap your hands behind your knees. Roll forwards until your feet tap the floor, then roll backwards to the point before your head touches the floor.
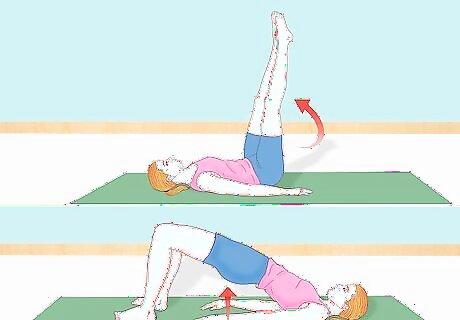
Develop core strength. Having toned muscles in your torso can help stabilize your spine, which should reduce the risk of injury during gymnastic moves like the chest roll. Core strength will also improve your range of movement and your balance/stability. Practice a supine bridge - lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Without using your hands, raise your hips so that your head, shoulders, arms, and feet are the only parts touching the floor. Do pelvic thrusts - lie on your back with your legs in the air at a 90 degree angle. Plant your hands and forearms flat at your sides and slowly lift your hips off the floor, controlling the movements as you raise and lower your lower body.














Comments
0 comment