views
General Troubleshooting
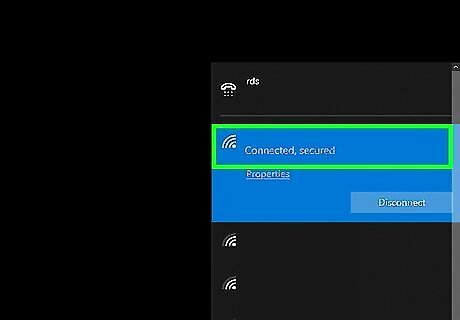
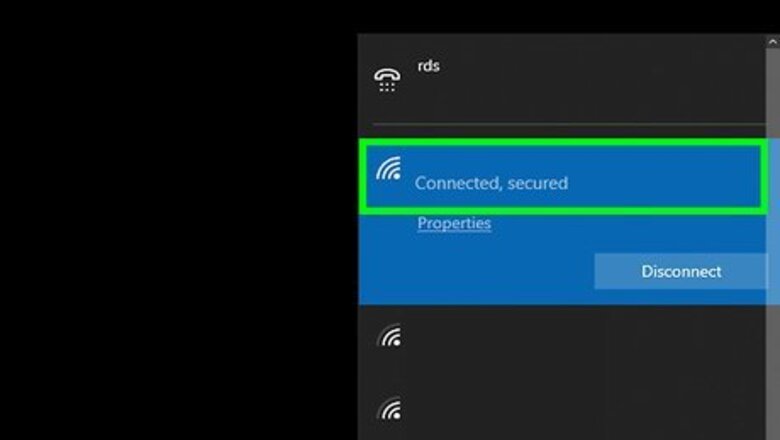
Check your Wi-Fi connection on your devices. Most internet-connected devices have a symbol that resembles a dot with arching lines on the display to indicate your Wi-Fi connection and strength. The more arching lines displayed, the stronger your Wi-Fi connection. If one device is not getting no or a poor Wi-Fi signal, the problem is most likely with the device. If it is happening on all devices, it is most likely a problem with your internet service. You can find the Wi-Fi symbol in the following locations on the following devices. Windows: In the task bar in the lower-left corner. Mac. In the menu bar in the upper-right corner. Smartphones and Tablets: In the upper-right corner of the screen.
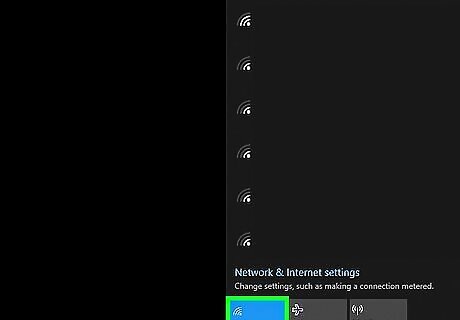
Make sure Wi-Fi is turned on. Click or tap the Wi-Fi icon on your computer or smart device. Check to make sure Wi-Fi is turned on in the Wi-Fi menu.
Check different internet services or websites. If one particular website or app is not working properly, it may be a problem with the app or website. Check other apps and websites to see if you are able to connect to them. If you can connect to other websites or services, the problem is with the website, not your internet connection. If you can't connect to any website or internet service, the problem is most likely with your internet connection.
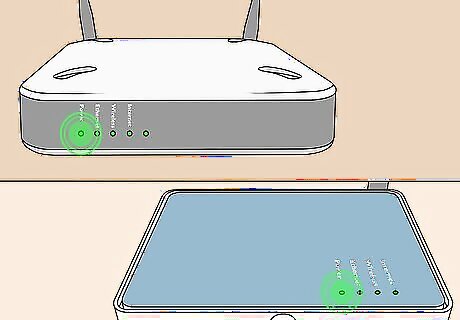
Check the lights on your modem or router. Most routers and modems have a light labeled "Internet", "WAN" or a symbol of a globe. This light should be solid white or green. If this light is flashing constantly, off, or red, this indicates that your router is not getting a proper signal. The lights on your router may be different from one router make and model to the next. If you are confused as to what the lights mean, check your user's manual or manufacturer's web page for more information.
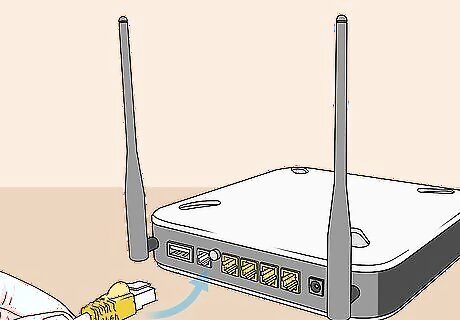
Make sure your internet cable is firmly attached to your modem or router. Check the back of your modem or router. Make sure your DSL phone line or coaxial cable is firmly connected to the modem or router.
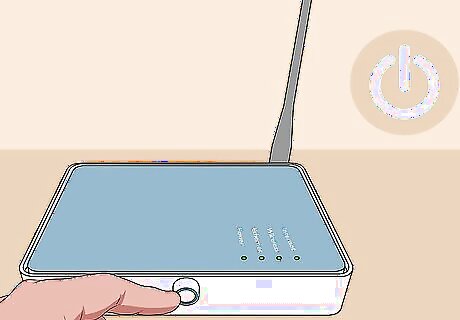
Restart your modem or router. If router settings are as they should detach the power cord from the router, wait for 1 minute and plug it in again. Wait 5 minutes for it to fully boot back up. The lights on the modem or router should turn solid when it is connected to the internet.
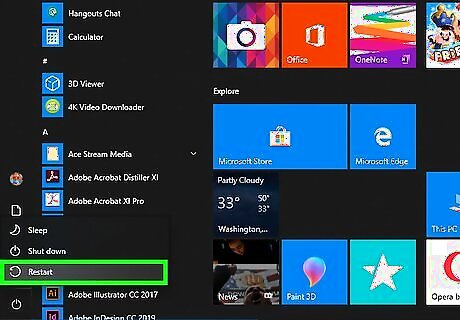
Restart your internet-connected devices. Sometimes restarting your internet-connected devices can fix network problems with individual devices.
Move your wireless devices closer to your modem or router. If you find that your devices lose their internet connection when they move away from your modem or router, try moving them closer. If the range or your wireless internet is a problem, you can expand your network using a second wireless router or you can purchase a wireless mesh system to expand the range of your wireless network.
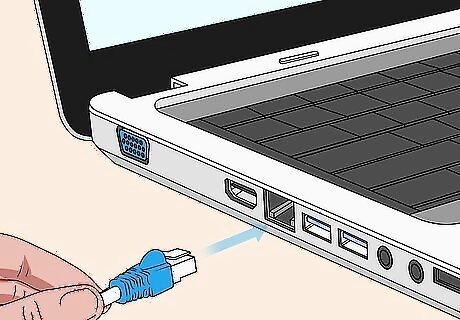
Use a wired connection. A wireless connection is more convenient, but a wired connection is more reliable. If you are having problems with your wireless internet connection, try connecting your computers, game consoles, and smart TVs to your router using an Ethernet cable.
Wait a couple of hours and try again. Sometimes internet traffic can overwhelm your internet service resulting in slow internet speeds and poor connections. Try again in a few hours and see if the issue is resolved. Make a note if you notice internet problems are happening at certain times of the day.

Call your internet service provider. Sometimes problems with your internet connection are the problem with your internet service provider. There may be an outage in your area, or maybe you forgot to pay the bill. Contact your internet service provider to see if there is a known problem with your internet connection, or to report a problem. One last simple fix can be reverting your router back to factory settings.
Windows
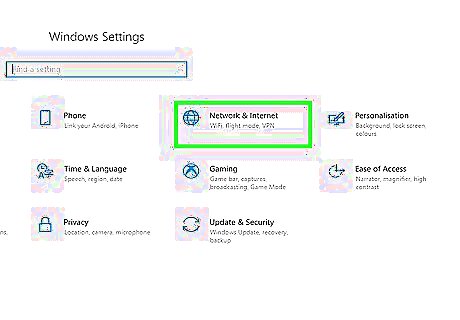
Check your network connection settings. If you recently updated your computer, your network connection settings may have changed. Use the following steps to check these settings: Click the Windows Start menu. Click the Settings menu/Gear icon. Click Network and Internet. Click Change adapter options. Click your internet connection. Click Diagnose this connection.
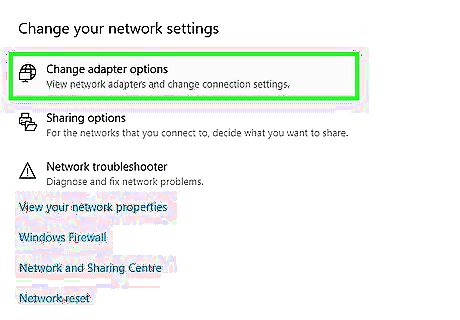
Fix an intermittent internet connection. If your network connection disconnects from time to time, your network adapter may be set to “power-saving” mode. To turn off the mode: Click the Windows Start menu. Click the Settings menu/Gear icon. Click Network and Internet Click Change adapter options. Right-click on the connection and then select Properties. Locate the Networking tab and click Configure. Click the Power Management tab. Uncheck the box next to “Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power.” Click Ok.
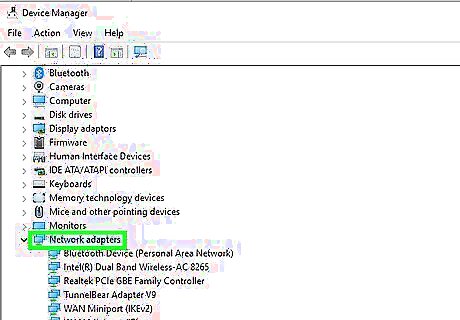
Update your Windows drivers. Ensuring your network drivers are up-to-date can solve a lot of problems. Use the following steps to update your network drivers. Click the Windows Start menu. Type "Device Manager" and click the Device Manager icon. Double-click Network Adapters . Right-click a network adapter. Click Update Driver. Click Search automatically for updated driver software.
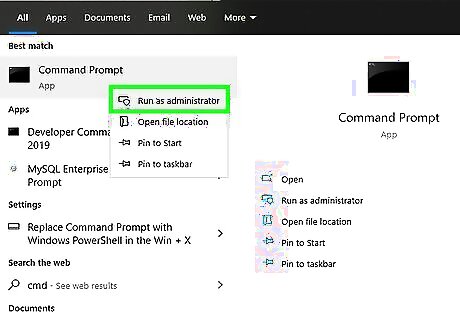
Turn off autotuning. The autotuning feature automatically resizes TCP windows. Disabling autotuning will limit the size of the TCP window to 65535 and increase the speed of your internet connection. Click the Windows Start icon Type “cmd” into the search box. Right-click on the Command Prompt icon and click Run as Administrator. Type the following into the text box: "netsh interface TCP set global autotuninglevel=disabled". Hit the Enter key. Restart your computer.
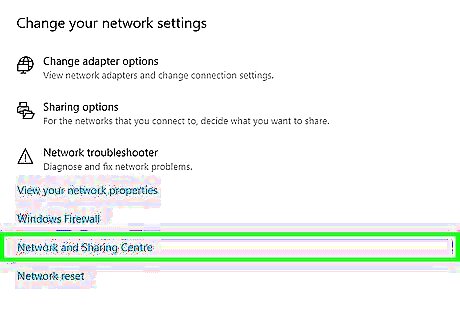
Enable Network Sharing. Make sure that the computer you are trying to connect to is on and that file and printer sharing is enabled on both computers. Use the following steps to turn on Network Sharing: Click the Windows Start icon. Click the Settings menu/Gear icon. Click Network and Internet. Click Network and Sharing Center. Click Change Advanced Sharing settings: Click Turn on Network Discovery. Click Turn on file and printer sharing. Click Save changes.
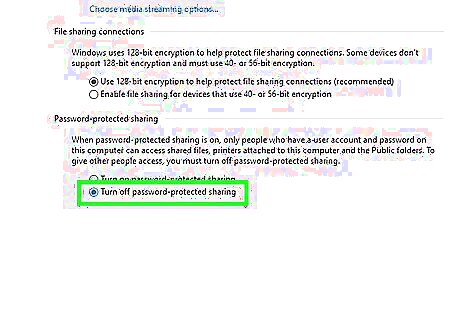
Override or turn off password protected sharing. Use the following steps to turn off password protected sharing on all computers on the network: Click the Windows Start menu. Click the Settings menu/Gear icon. Click Network and Internet. Click Network and Sharing Center. Click Change Advanced Sharing settings: Scroll down and click All Networks. Click Turn off password protected sharing. Click Save changes.
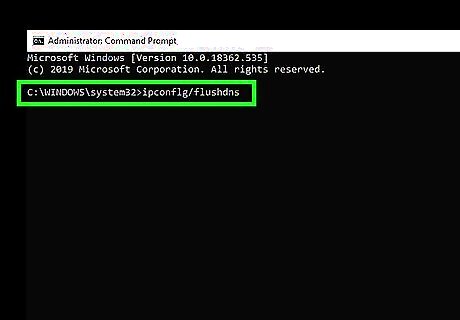
Clear your DNS cache. If you are repeatedly receiving error messages when trying to access a website, you may need to erase your DNS cache. Use the following steps to clear your DNS cache: Click Windows Start" Type “cmd” into the search box. Right-click on the Command Prompt icon and select Run as Administrator. Type “ipconfig/flushdns” in the command prompt. Press Enter.
Mac
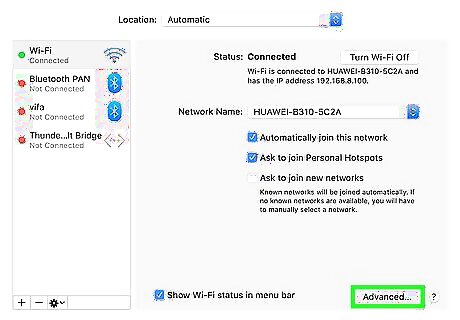
Set your Mac to automatically join your wi-fi network. If you have to enter your wi-fi password every time you want to access the internet, your computer is not remembering your network. Use the following steps to correct this: Click on the WiFi icon in the top left corner of your screen. Click on Open Network Preferences. Click your internet connection. Click Advanced. Check the box next to “Remember networks this computer has joined." Click Ok.
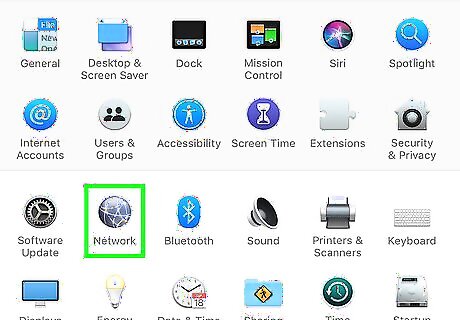
Overcome an intermittent internet connection. If your internet connection repeatedly and randomly cuts in and out, you can fix this issue by configuring your Mac to connect to a 5 GHz network instead of a 2.4 GHz network. The 5GHz network has a shorter range but has less interference. Use the following steps to configure your network settings: Click on the Apple icon in the upper-left corner. Click System Preferences. Click on the Network icon that resembles a globe. Click Advanced. Scroll through your list of Networks until you find your 5 GHz network. Click on this network and drag it to the top of the list.
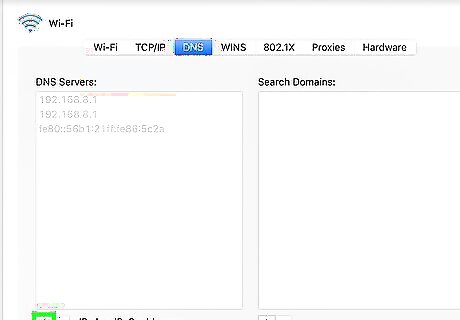
Correct for slow internet by altering your DNS. DNS, or Domain Name System, translates a web address into an IP address and stores the information on your computer. Your computer automatically uses the DNS associated with your router. For faster processing times, you can manually change your DNS to one of two free providers: Open DNS or Google DNS. Use the following steps to change your DNS server settings: Click on the Apple icon in the upper-left corner. Click System Preferences. Click on the Network icon that resembles a globe. Click Advanced. def Select your network from the list and then open the “DNS” tab. Click on the “+” icon under the “DNS Servers” column. Enter in an IP address for a free DNS server. OpenDNS: 208.67.222.222 or 208.67.220.220. Google DNS: 8.8.8.8 or 8.8.4.4. Click Ok Click Apply.
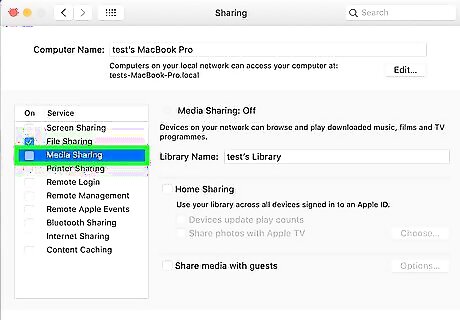
Resolve home sharing issues. Home sharing allows multiple devices, including computers, tablets, and Apple TVs, to connect to and utilize the files on your computer. Make sure all of the devices you want to share with use the same Apple ID and password. If you are having trouble with this function, try the following: macOS Catalina and later: Click the Apple icon. Click System Preferences Click Sharing Check Media Sharing. Enter your Apple ID password. macOS Mojave and earlier: Launch iTunes. Enter your Apple ID and password. Click File Click Home Sharing. Turn on Home Sharing.




















Comments
0 comment